Figure 5.
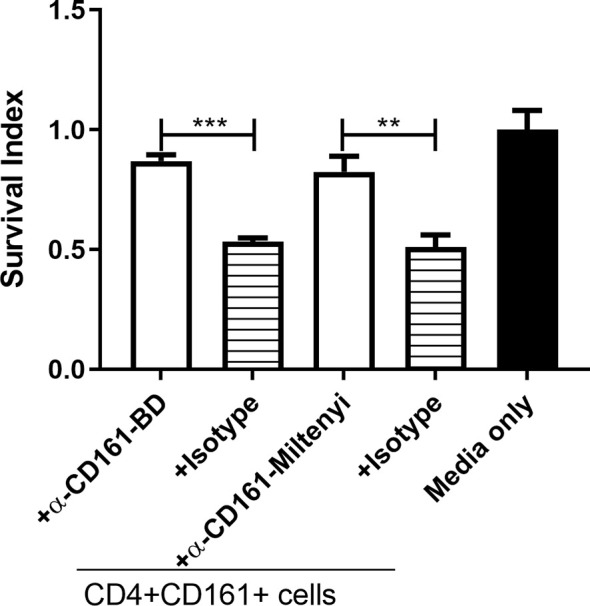
CD161 blockade reduced the ability of primaryCD4+CD161+T cells to inhibit intracellular mycobacterial growth. Shown are bar graph data of Survival indexes for BCG bacilli in infected hMDM alone or co-cultured with primaryCD4+CD161+ T cells plus infected hMDM co-cultured for 72 h at a ratio of 10:1 in the absence or presence of two anti-CD161 mAbs (5 ug/ml for each) or corresponding Ig isotype controls (5 ug/ml for each). Note that anti-CD161 neutralizing mAbs from two sources (BD and MACS), not isotype controls, could each reverse the ability of CD4+CD161+ T cells to inhibit intracellular mycobacterial growth. Data were pooled from three independent experiments involving 10 healthy donors. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01 (ANOVA, Tukey’s test).
