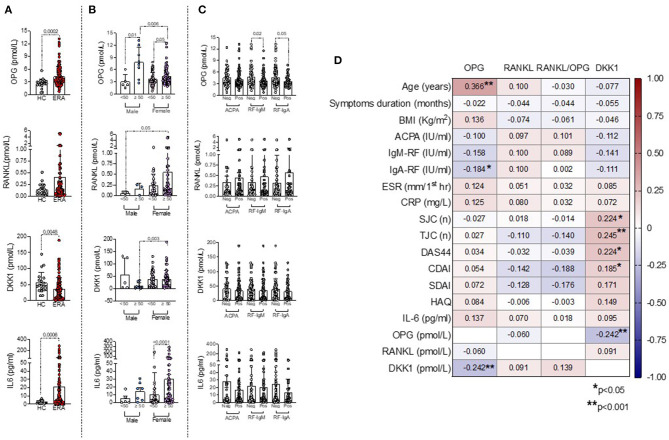
Figure 2.
(A–D) Associations between bone-derived biomarkers with clinical and immunological features in ERA patients at disease onset. (A) OPG, RANKL, DKK1, and IL-6 plasma levels at baseline in ERA patients and HC, Mann–Whitney U test. (B) OPG, RANKL, DKK1, and IL-6 plasma levels at baseline in ERA patients stratified based on sex and age categories, Mann–Whitney U test. (C) OPG, RANKL, DKK1, and IL-6 plasma levels at baseline in ERA patients stratified based on individual ACPA, IgA/IgM-RF positivity, Mann–Whitney U test. (D) Heatmap showing the correlations between bone-derived biomarkers and RA features, Spearman rank correlation test. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. ERA, early rheumatoid arthritis; OPG, osteoprotegerin; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa beta; DKK1, Dickkopf-1; ACPA, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies; IgA/IgM-RF, immunoglobulin A or immunoglobulin M isotypes rheumatoid factor; BMI, body mass index; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C-reactive protein; SJC, swollen joint count; TJC, tender joint count; DAS44, Disease Activity Score measured on 44 joints; CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; SDAI, Simple Disease Activity Index; HAQ, Health Assessment Questionnaire; IL-6, interleukin-6.