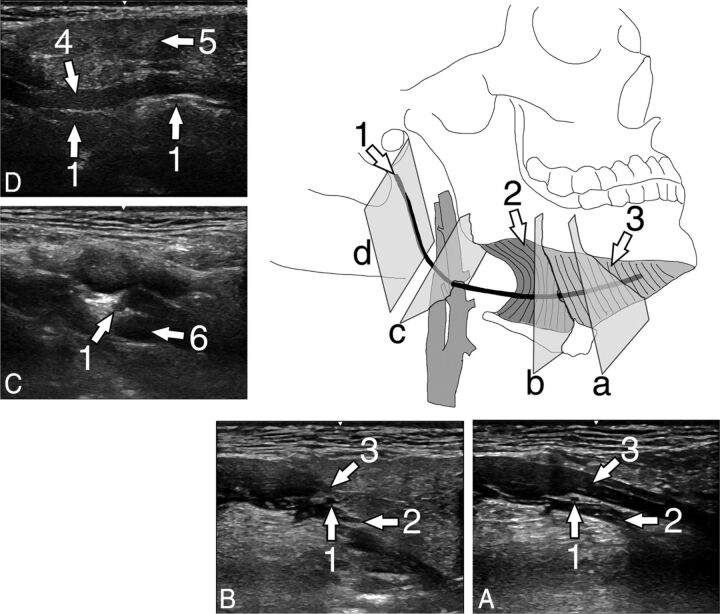
Fig 1.
Illustration of the hypoglossal nerve with exemplary US scans of the hypoglossal nerve of a healthy volunteer. A, Transversal scan at the floor of the mouth in a coronal body plane. B, Transversal scan at the posterior rim of the hyoglossal muscle in a coronal body plane. C, Transversal scan in a paracoronal body plane at the crossing of the nerve with the external carotid artery. D, Longitudinal scan at the carotid space in a paracoronal body plane. 1 = hypoglossal nerve, 2 = hyoglossal muscle, 3 = mylohyoid muscle, 4, = stylohyoid and styloglossal muscles, 5 = parotid gland, 6 = external carotid artery.