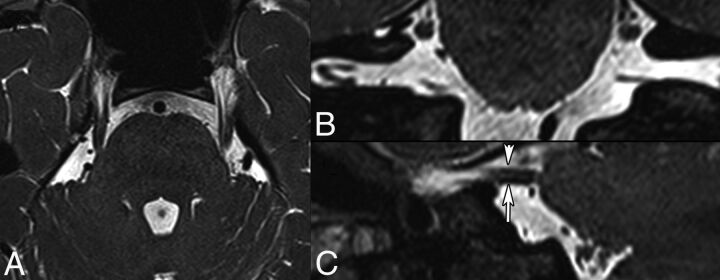
Fig 2.
Normal anatomy of the cisternal segment of CN V obtained at 3T. Axial 0.6-mm thin-section (A), coronal (B), and sagittal (C) 2D reconstructions (same thickness) from a 3D T2-weighted balanced steady-state free precession sequence. Note that multiple individual nerve fibers can be identified in both cisternal CN Vs. The short arrow in C points to the motor root of the left CN V, while the long arrow points to the sensory root.