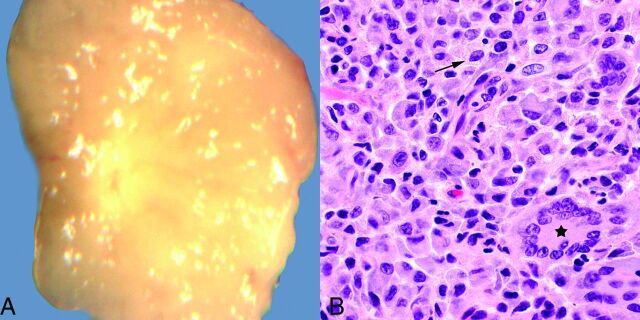
Fig 1.
A, Grossly, juvenile xanthogranulomas are typically yellowish, due to their high lipid content. B, Hematoxylin-eosin stain, original magnification ×600. Microscopically, abundant variably lipidized histiocytes are present (arrow), usually with admixed Touton giant cells (star) and scattered inflammatory cells (not shown on this image).