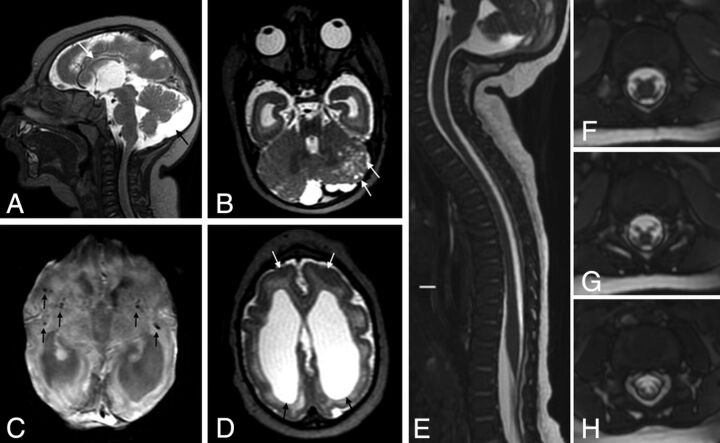
Fig 5.
MR imaging of the brain and the spinal cord of an infant with microcephaly confirmed to be caused by the Zika virus without arthrogryposis. Sagittal T2-weighted images (A) shows hypogenesis of the corpus callosum (white arrow) and an enlarged cisterna magna (black arrow). Coronal T2-weighted image (B) shows left cerebellar hemisphere hypoplasia, with cortical malformation and microcysts (white arrows). Axial SWI (C) shows small dystrophic calcifications in the junction between the cortical and subcortical white matter and in the basal ganglia (black arrows). Axial T2-weighted image (D) shows a simplified gyral pattern, bilateral cortical thickness in the pachygyric frontal lobe (white arrows), and ventriculomegaly (black arrows). The spinal cord and conus medullaris are normal-sized and show no abnormal signal on the sagittal T2-weighted volumetric GRE (E). Axial reformatted T2-weighted volumetric GRE reveals normal-sized anterior and posterior nerve roots in the conus medullaris (F and G) and cauda equina (H).