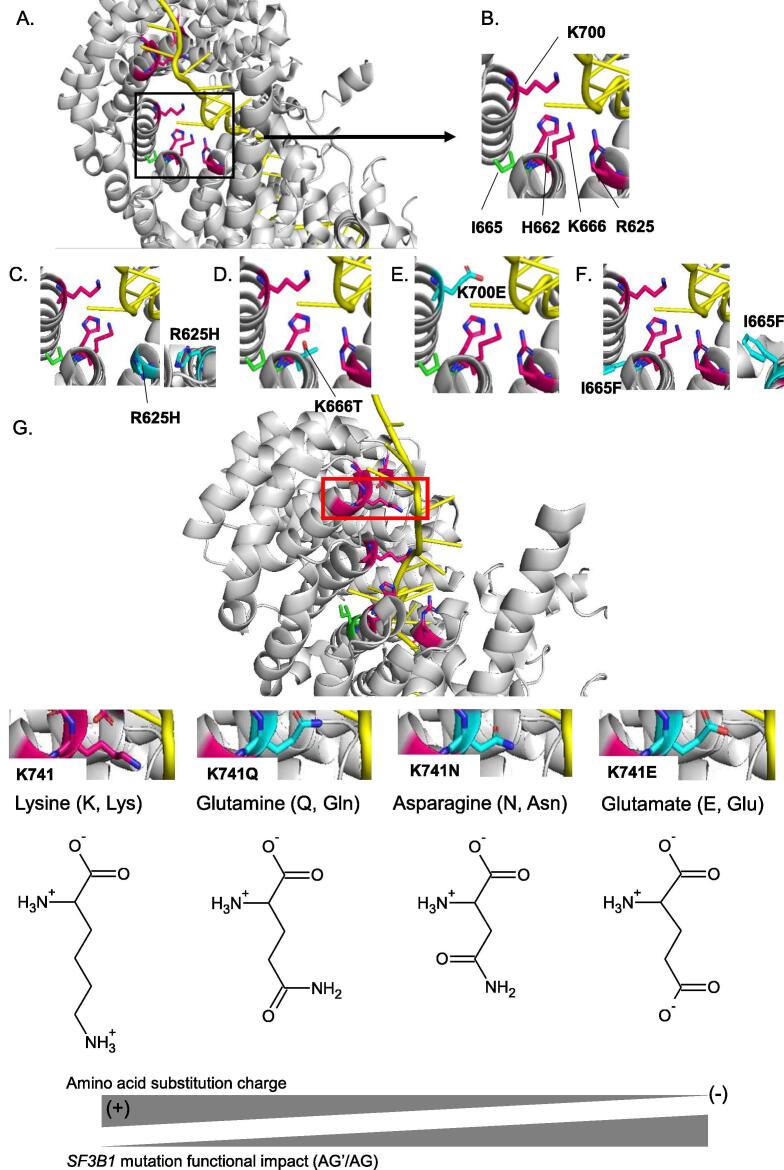
Fig. 4.
Structural impact of amino acid substitutions of SF3B1 in the activated spliceosome (Bact complex) (PDB ID: 5Z56). A. Overview of wild-type SF3B1 amino acids (R625, H662, I665, K666, K700, G740, K741, G742, D781) with a zoom (black box) on the hotspot region (R625, H662, I665, K666 and K700E). The amino acids susceptible to damaging substitutions are R625, H662, K666, K700, G740, K741, G742, D781 and their carbon chains are represented in pink. The carbon chain of the amino acid I665 susceptible to substitution with no functional impact is represented in green. B-F. A zoom on the amino acids R625, H662, I665, K666 and K700 (B) and the corresponding mutations R625H (C), K666T (D), K700E (E) and I665F (F). The carbon chains of substitutions are represented in light blue. G. Representation of wild-type SF3B1 amino acids (R625, H662, I665, K666, K700, G740, K741, G742, D781) and an overview (red box) of the residue K741. The amino acids susceptible to damaging substitutions are R625, H662, K666, K700, G740, K741, G742, D781 and their carbon chains are represented in pink. The carbon chain of the amino acid I665 susceptible to substitution with no functional impact is represented in green. A zoom on the amino acid K741 and its substitutions K741Q, K741N and K741E. The carbon chains of substitutions are represented in light blue. (+): positively charged amino acid; (-): negatively charged amino acid. Oxygen (O), nitrogen (N) and pre-mRNA are shown respectively in red, dark blue and yellow. The residues are shown as stick in elemental colors and the figure was rendered using PyMOL. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)