Abstract
Background
Over the past 20 years prescription of opioid medicines has markedly increased in the UK, despite a lack of supporting evidence for use in commonly occurring, painful conditions. Prescribing is often monitored by counting numbers of prescriptions dispensed, but this may not provide an accurate picture of clinical practice.
Aim
To use an estimated oral morphine equivalent (OMEQe) dose to describe trends in opioid prescribing in non-cancer pain, and explore if opioid burden differed by deprivation status.
Design & setting
A retrospective cohort study using cross-sectional and longitudinal trend analyses of opioid prescribing data from Welsh Primary Care General Practices (PCGP) took place. Data were used from the Secure Anonymised Information Linkage (SAIL) databank.
Method
An OMEQe measure was developed and used to describe trends in opioid burden over the study period. OMEQe burden was stratified by eight drug groups, which was based on usage and deprivation.
Results
An estimated 643 436 843 milligrams (mg) OMEQe was issued during the study. Annual number of prescriptions increased 44% between 2005 and 2015, while total daily OMEQe per 1000 population increased by 95%. The most deprived areas of Wales had 100 711 696 mg more OMEQe prescribed than the least deprived over the study period.
Conclusion
Over the study period, OMEQe burden nearly doubled, with disproportionate OMEQe prescribed in the most deprived communities. Using OMEQe provides an alternative measure of prescribing and allows easier comparison of the contribution different drugs make to the overall opioid burden.
How this fits in
It is known that opioid prescribing has increased in the UK over the past 20 years. Measures of prescribing vary and are not always reflective of what is seen in practice, nor do they allow easy identification of populations or individuals most at risk. This study used an OMEQe to standardise prescribing data. It demonstrated anomalies in prescription numbers and opioid burden. The use of OMEQ provides more easily comparable data across a range of opioid medicines and warrants consideration as a standard measure of prescribing.
Introduction
The number of prescriptions for opioid medicines issued in the UK has increased substantially over the past 20 years.1–6 In particular, prescriptions for ‘strong’ opioids, such as morphine, oxycodone, and fentanyl, have seen greater increases than those classed as ‘weak’, such as codeine and dihydrocodeine.1,2,6 Prescribing continued to increase even when evidence to support using these medicines for people living with non-cancer pain is largely absent.7–11
National and international concerns have focused on strong opioids.12–14 However, dose and duration of use are more likely indicators of harm or potential for dependence than the choice of drug itself.11,15–20 It has been estimated that adverse events occur in as many as 78% of people using opioids over extended periods of time.11–13 Higher doses14–17 have been associated with depression and anxiety,18–20 and an increased risk of dependence and misuse.21–24 It has been proposed the burden or risk of opioids would be more accurately discussed in mg doses or dose equivalents, rather than number of prescriptions alone.2,25
An accurate estimation of opioid burden and risk is especially important in areas of high socioeconomic deprivation, which are associated with poorer health outcomes, higher incidence of chronic pain,2,26,27 and mental health disorders compared with the general population.28 Deprivation is associated with higher prescribing of potentially dependence-forming medicines, including opioids, especially for chronic, non-cancer pain in the UK29 and internationally.30 Furthermore, concomitant use of other medicines, such as benzodiazepines and antidepressants with opioids, have also been disproportionately reported in more deprived areas and confer additional risk of harm to the user.31–33
Wales has historically high levels of deprivation.34 In 2016, 23% of the Welsh population lived in poverty, more than in England (22%), Scotland (19%), or Northern Ireland (20%).35 The south of the country contains the majority of the most deprived areas in Wales,36 and also has the highest opioid-related death rates in England and Wales.29 However, only one comprehensive analysis of Welsh opioid prescribing has been undertaken.4
The aim of this study was to examine opioid prescribing trends in Wales between 2005 and 2015 using an estimated measure of daily OMEQ dose to standardise data. Analysis of OMEQe by deprivation quintile determined if opioid burden varied in distinct areas of socioeconomic deprivation.
Method
Data source
The study used individuals' anonymised data held in the SAIL databank, which is part of the national e-health records research infrastructure for Wales.37,38
Each individual was allocated a unique anonymised linkage field (ALF) number. The ALF allowed cross-linking between different existing datasets, providing a record of all healthcare interactions for each individual whose data is available to SAIL. A dataset was produced by cross-linking individuals’ anonymised records from the PCGP and Welsh Index of Multiple Deprivation (WIMD) 2011 datasets, based on the local super output areas (LSOAs) contained within the PCGP dataset.
At the time of this study, the databank contained complete data from 1 January 2005–31 December 2015 and so 11 years of available data were examined.
Opioid prescriptions
Prescriptions are automatically assigned Read codes on the electronic patient record, when issued in primary care, providing consistent identification of data.1,3,37,38 Read codes are a thesaurus of clinical terms used to record interactions, diagnoses, and interventions in primary care settings in Wales. A list of Read codes was compiled for all prescribable oral and transdermal opioid medicines used for analgesia, including combination products, for example, paracetamol and codeine (co-codamol), using the NHS Information Authority’s clinical terminology browser. Products licensed for the management of misuse and injectable opioids, which are reserved for palliative care, were excluded.
Only data for people aged ≥18 years between 2005 and 2015 without a recorded cancer diagnosis (identified using Read codes for cancer diagnoses or treatment) at any time between 2004 and 2015 were included in the analysis.
All data were subjected to repeated cross-sectional sampling to determine prescribing trends over the study period.
Estimated oral morphine equivalent dose
At the time of this study, dispensing data were not included within SAIL datasets. The prescribed drug product, including strength, was available from PCGP data, but not administration directions and quantity of each opioid product prescribed. Therefore, actual oral morphine equivalent dose for each individual could not be calculated.
An OMEQe measure was developed using data available from SAIL (Table 1). For each product, the recommended daily dose per day was taken from the British National Formulary 39 and electronic medicines compendium (emc).40 The daily dose was converted to a daily OMEQe value, based on available conversion tables.8,39 Daily OMEQe for each product was multiplied by the number of prescriptions issued each year to determine annual totals (Table 1). Results were stratified by drug, with less frequently prescribed medicines (oral diamorphine, dipipanone, hydromorphone, meptazinol, methadone tablets, pentazocine, pethidine, and tapentadol) grouped as ‘other’ opioids.
Table 1. Example of calculations for OMEQe (mg) using 2005 data for female subjects.
| Units used for calculating annualised OMEQe | ||||
| Drug product | Recommended daily dosea ,b | Oral morphine equivalent of daily dose (mg)c ,d | Annual number of prescriptions | Annualised total OMEQe burden (mg) |
| Buprenorphine | ||||
| 10 mcg per hour | 1 patch per week | 24 | 28 | 672 |
| 52.5 mcg per hour | 1 patch twice a week | 126 | 354 | 44 604 |
| Codeine | ||||
| Co-codamol 8/500 | 2 tablets 4 times a day | 6.4 | 17 952 | 114 893 |
| Codeine phosphate 30 mg | 2 tablets 4 times a day | 24 | 16 293 | 391 032 |
| Zapain capsules (30/500) | 2 tablets 4 times a day | 24 | 112 | 2688 |
| Dihydrocodeine | ||||
| Co-dydramol 10/500 | 2 tablets 4 times a day | 8 | 153 047 | 1 224 376 |
| DHC Continus 90 mg MR tablet | 1 tablet twice a day | 18 | 1009 | 18 612 |
| Remedeine tablet | 2 tablets 4 times a day | 16 | 1295 | 20 720 |
| Fentanyl | ||||
| Durogesic 100 mcg per hour patch | 1 patch every 3 days | 360 | 131 | 47 160 |
| Fentanyl 200 mcg SL lozenge | 1 lozenge 4 times a day | 120 | 40 | 4800 |
| Fentanyl 25 mcg per hour patch | 1 patch every 3 days | 90 | 3429 | 308 610 |
| Morphine | ||||
| Morphgesic SR 10 mg m/r tablet | 1 tablet twice a day | 20 | 73 | 730 |
| MXL 60 mg m/r capsule | 1 capsule once a day | 60 | 23 | 1380 |
| Oramorph 10 mg/5 ml liquid 100 ml | 5 mL every 2 hours | 120 | 573 | 68 760 |
| Sevredol 20 mg tablet | 1 tablet every 6 hours | 120 | 299 | 35 880 |
| Oxycodone | ||||
| Longtec 20 mg m/r tablets | 1 tablet twice a day | 80 | 1 | 80 |
| Oxycodone HCl 20 mg capsule | 1 capsule every 4 hours | 240 | 250 | 60 000 |
| OxyContin 80 mg m/r tablet | 1 capsule twice a day | 320 | 262 | 83 840 |
| Tramadol | ||||
| Dromadol XL 200 mg m/r tablet | 1 tablet once daily | 20 | 11 | 220 |
| Tramadol 50 mg capsule | 2 capsules 4 times a day | 40 | 93 918 | 3 756 720 |
| Tramacet 325 mg/37.5 mg | 2 tablets 4 times a day | 30 | 4450 | 133 500 |
| Other | ||||
| Co-proxamol 32.5 mg/325 mg tablet | 2 tablets 4 times a day | 26 | 82 015 | 2 132 390 |
| Hydromorphone HCl 1.3 mg capsule | 1 capsule every 4 hours | 58.5 | 6 | 351 |
| Pethidine HCl 50 mg tablet | 1 tablet every 4 hours | 30 | 2381 | 71 430 |
Measuring utilisation
The number of prescriptions and number of patients per year were calculated per drug in repeat cross-sections for each year and further stratified by deprivation quintile. Data were standardised to annual population size for the SAIL databank, using data from the Office for National Statistics (ONS)41 and StatsWales.42 Deprivation data were adjusted by each quintile’s annual population.42
Data analysis
Data were extracted from the study tables within SAIL using Structured Query Language (SQL) code. Percentage change rate of number of prescriptions issued and number of people receiving prescriptions over the study period were also noted. Data were stratified into eight drug groups.
Shapiro-Wilk calculations showed data were non-parametric. Therefore, Kruskal-Wallis tests were used to examine differences in mean prescribing over the study period in the different drug groups and deprivation quintiles. Statistical analysis was conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics software (version 25.0) and figures drawn using Excel (version 16.30; retrieved from https://office.microsoft.com/excel).
Deprivation scores
The WIMD is the official measure used by Welsh Government to determine relative deprivation of areas within Wales.36 The WIMD is a weighted total score of deprivation based on income (23.5%), employment (23.5%), health (14%), education (14%), geographical access of services (10%), community safety (5%), physical environment (5%), and housing (5%). Scores are not linear, so areas in group two are not twice as deprived as those in group four. Indices are published every 3 years.43 The 2011 index was recommended by SAIL for use in this study, as representative of the full 11-year period. There were no significant changes in LSOA or WIMD areas in that time. Data are presented in quintiles, with WIMD1 being the most deprived areas and WIMD5 the least deprived.
Results
Prescribing data were extracted from 345 PCGPs across Wales. A total of 22 641 424 prescriptions for opioids were included in the analysis. Between 2005 and 2015, opioid prescriptions increased by 44% from 692 to 994 prescriptions per 1000 population annually. The total daily OMEQe, issued from all included practices in Wales, more than doubled in the 11 years examined, from 37 662 651 mg to 76 428 768 mg. When adjusted to population, annualised daily OMEQe per 1000 population increased by 95% (from 16 266 mg to 31 665 mg) over the study period (Table 1).
Total estimated oral morphine equivalent prescribed
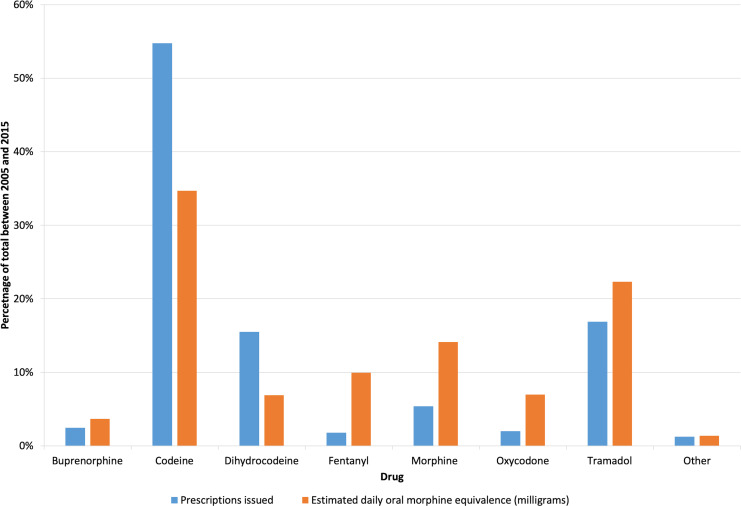
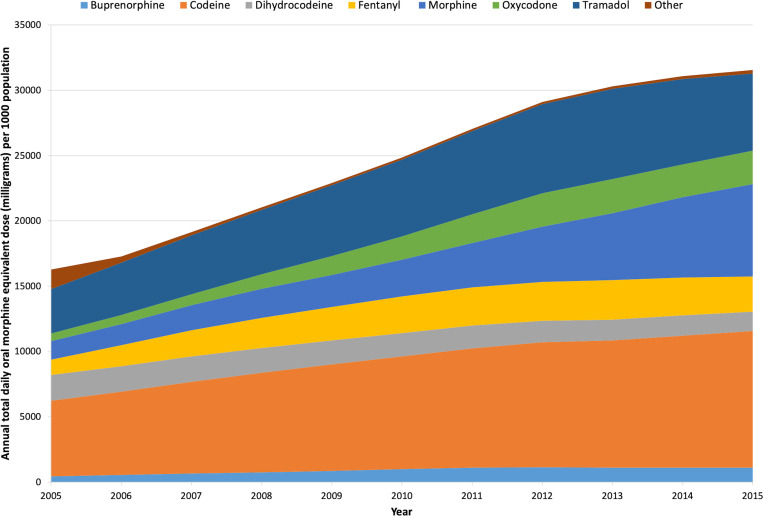
Codeine was the most commonly prescribed opioid (Table 2), with just under 12.5 million prescriptions issued and the highest annual total OMEQe prescribed for the study duration (Figure 1). Codeine OMEQe per 1000 population increased by 79%, from 5916 mg to 10 581 mg. Tramadol was the second most commonly prescribed opioid in Wales with a 74% increase, from 3397 mg to 5905 mg OMEQe per 1000 population, although annual total OMEQe started to reduce from 2014 (Figure 2).
Table 2. Daily OMEQe (mg) issued on prescription, given as annual totals and adjusted to population, stratified by drug.
| Oral or transdermal opioids | ||||
| Total daily OMEQe (mg) dose prescribed | Annual total daily OMEQe dose (mg) per 1000 population | OMEQe dose (mg) per prescription issued | Annual number of prescriptions issued per 1000 population | |
| Buprenorphine | 23 641 528 | |||
| 2005 | 977 464 | 422 | 98 | 4 |
| 2015 | 2 756 458 | 1142 | 37 | 31 |
| Rate change, % | 182 | 170.5 | –61.7 | 606.3 |
| Codeine | 223 817 156 | |||
| 2005 | 13 743 115 | 5916 | 17 | 357 |
| 2015 | 25 593 382 | 10 581 | 19 | 549 |
| Rate change, % | 86.2 | 78.8 | 16.2 | 53.9 |
| Dihydrocodeine | 44 600 874 | |||
| 2005 | 4 368 806 | 1887 | 12 | 154 |
| 2015 | 3 471 460 | 1438 | 13 | 109 |
| Rate change, % | –20.5 | –23.8 | 7.7 | –29.2 |
| Fentanyl | 64 138 905 | |||
| 2005 | 2 695 290 | 1164 | 186 | 6 |
| 2015 | 6 496 270 | 2691 | 147 | 18 |
| Rate change, % | 141.0 | 131.2 | –21.2 | 193.2 |
| Morphine | 91 132 530 | |||
| 2005 | 3 293 220 | 1422 | 86 | 17 |
| 2015 | 17 047 800 | 7063 | 68 | 104 |
| Rate change, % | 417.7 | 396.6 | –20.6 | 525.6 |
| Oxycodone | 45 120 680 | |||
| 2005 | 1 316 480 | 569 | 105 | 5 |
| 2015 | 6 165 400 | 2554 | 100 | 26 |
| Rate change, % | 368.3 | 349.3 | –4.9 | 372.4 |
| Tramadol | 144 173 635 | |||
| 2005 | 7 865 695 | 3397 | 36 | 95 |
| 2015 | 14 252 335 | 5905 | 38 | 156 |
| Rate change, % | 81.2 | 73.8 | 5.7 | 64.4 |
| Other | 8 888 696 | |||
| 2005 | 3 446 735 | 1719 | 27 | 56 |
| 2015 | 699 711 | 347 | 58 | 5 |
| Rate change, % | –79.7 | –79.8 | 117.4 | –91.0 |
Results are rounded to nearest whole number. Rate change (%) calculated using original, unrounded data. Original data are available from the authors on request.
Figure 1. Comparison of the percentage contribution of each opioid prescribed by total prescriptions issued and total daily OMEQe dose (mg) in Wales between 2005 and 2015.
Figure 2. Trends in opioid prescribing across Wales, 2005–2015. Annual daily OMEQe in mg per 1000 population, stratified by drug.
Large increases were noted in ‘strong’ opioids (morphine, oxycodone, fentanyl, and buprenorphine) during the study (Figure 2). Morphine OMEQe increased by 397%, from 1422 mg to 7063 mg per 1000 population (Table 2). By 2015, morphine was prescribed at three times the equivalent dose of either oxycodone (increased 349%, from 569 mg to 2554 mg per 1000 population) or fentanyl (increased 131%, from 1164 mg to 2691 mg per 1000 population).
Overall, 71% of the total opioid burden in the areas of Wales covered by the SAIL databank was accounted for by three drugs: codeine (35%), tramadol (22%), and morphine (14%). Statistically significant differences were found between the 11-year total OMEQe when each drug group was compared with the others (P<0.001, H = 73.5, ฦ2 = 0.8).
Opioid prescribing trends by deprivation
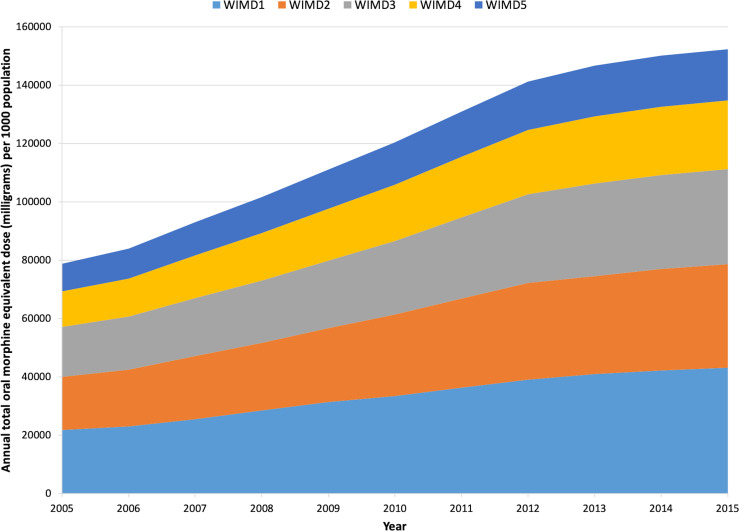
Figure 3 illustrates the trends in annualised daily OMEQe of all oral and transdermal opioids stratified by the WIMD (2011). Over the study, people in the most deprived quintiles (WIMD1) were prescribed an estimated 100 711 696 mg more OMEQe than in the least deprived (WIMD5) (Table 3).
Figure 3. Trends in opioid prescribing across Wales, 2005–2015. Annual daily OMQEe (mg) per 1000 population, stratified by deprivation. Welsh Index of Multiple Deprivation 2011 (WIMD 2011), where WIMD1 = most deprived, WIMD5 = least deprived.
Table 3. Trends in OMEQe (mg) prescribing stratified by deprivation.
| Oral or transdermal opioids | ||
| Deprivation quintile | Total daily OMEQe dose (mg) prescribed | Total daily OMEQe dose (mg) per 1000 population |
| WIMD1 | ||
| 2005 | 10 319 636 | 21 757 |
| 2015 | 21 167 919 | 43 176 |
| Rate change, % | 105.1 | 98.4 |
| Total prescribeda | 176 824 265 | |
| WIMD2 | ||
| 2005 | 8 590 375 | 18 203 |
| 2015 | 17 399 026 | 35 475 |
| Rate change, % | 102.5 | 94.9 |
| Total prescribeda | 146 459 878 | |
| WIMD3 | ||
| 2005 | 7 684 060 | 17 108 |
| 2015 | 15 342 942 | 32 564 |
| Rate change, % | 99.7 | 90.3 |
| Total prescribeda | 129 880 669 | |
| WIMD4 | ||
| 2005 | 5 374 595 | 12 242 |
| 2015 | 10 878 897 | 23 534 |
| Rate change, % | 102.4 | 92.2 |
| Total prescribeda | 93 691 687 | |
| WIMD5 | ||
| 2005 | 4 486 035 | 9 381 |
| 2015 | 8 721 170 | 17 557 |
| Rate change, % | 94.4 | 87.2 |
| Total prescribeda | 76 112 569 | |
aTotal prescribed 2005–2015. Annual OMEQe calculated as per method and stratified by deprivation quintile (Welsh Index of Multiple Deprivation [WIMD2011], where WIMD1 = most deprived, WIMD5 = least deprived). OMEQe = estimated oral morphine equivalent.
Between 2005 and 2015, OMEQe doubled in all but the least deprived (WIMD5) areas (Table 3). Twenty-eight per cent (176 824 265 mg of 622 969 068 mg) of total OMEQe was issued in the most deprived areas of Wales. In contrast, 12% (76 112 569 mg) were prescribed in the least deprived areas. Throughout the study, OMEQe prescribed in WIMD1 areas remained more than twice those noted in WIMD5 areas (Table 3) for both total OMEQe (mg) and OMEQe per 1000 population. Despite large percentage increases in all quintiles, the difference between total OMEQe prescribed per quintile were statistically significant (P<0.001, H = 34.5, ฦ2 = 0.61).
Discussion
Summary
This study identified trends in opioid prescribing in Wales, similar to those previously reported in other parts of the UK.1,3,6,26,27,44 A marked increase in opioid burden in Wales between 2005 and 2015 was noted. Using the OMEQe measure described, opioid burden in the study population nearly doubled in 11 years. Increasing deprivation was associated with higher OMEQe and, consequently, a higher burden per person, despite rises in percentage terms being similar in all WIMD 2011 quintiles.
Strengths and limitations
Large sets of prescribing and diagnostic data have been validated as an accurate means for conducting healthcare population research,45,46 as they reduce recall bias and regional variation. In this study, anyone registered with included practices and prescribed an opioid medicine were included in the analysis, avoiding selection bias. This is the first study of Welsh data to utilise OMEQe to better understand the burden of opioid prescribing on the population. Using linkage systems within SAIL datasets, data from people with a recorded cancer diagnosis could be excluded from analysis. The data confidently reflects prescribing for non-cancer pain, unlike other recent studies that assumed the majority of prescribing was attributable to persisting, non-cancer pain based on longevity of prescribing and dose forms used.2,6
Other studies have suggested large increases in prescribing are attributable to a range of drugs.2,6,47 The current study showed that three drugs were responsible for the majority of prescribing. This may, in part, be owing to the effective use of National Prescribing Indicators, which, in particular, have encouraged morphine to be used as first-line ‘strong’ opioid.48
Prescribing data provide an indication of intention to treat but does not confirm consumption. It also does not indicate the diagnosis or how long an individual might have been using the medication. Moreover, data presented here did not identify people receiving more than one opioid medicine and, so, would have higher individual OMEQe burdens.
It was not possible to access dispensing data, which provides details required to accurately calculate OMEQ. The authors' estimated measure (OMEQe) required assumptions to be made in regard of daily dose prescribed. Also, quantity could not be verified in order to calculate duration of use. However, the trends are similar to those reported elsewhere in the UK.1–3,6,27,44
Further analysis is required to determine an individual’s daily intake, where multiple opioids and strengths of products are prescribed. While prescription numbers have started to stabilise or reduce since the end of the study,6,48,49 concerns remain about the number of people receiving supramaximal opioid doses and lengthy durations of use.11,32
In the study, opioid medicines were identified by Read codes and accuracy of data extraction depended on the inclusivity of the coding used. Similar rationales for deciding which opioid products to include in analysis of primary care prescribing have been adopted by other UK-based authors.1,3,6,27 However, incomplete coding lists could result in an under-representation of prescribing.
Comparison with existing literature
Examining trends by prescription numbers alone is likely to underestimate the opioid burden within a population. Using English data, Curtis et al demonstrated a 34% growth in prescription numbers equated to a 127% increase in OMEQ burden between 1998 and 2016.6 In the present study, a 44% increase in prescription numbers in Wales, translated into a 95% increase in opioid burden using the OMEQe measure described.
Another measure of prescribing is defined daily doses (DDD), devised by the World Health Organization:50 DDDs are ‘ the assumed average maintenance dose per day for a drug used for its main indication in adults . ’ However, DDDs vary for each drug and between formulations of the same drug.50 When OMEQ was used to compare prescribing in four Nordic countries, it demonstrated noteworthy differences in patterns of opioid consumption compared with those seen with DDDs.43 ‘Weak’ opioids, such as codeine, carry higher DDD values than ‘strong’ opioids like morphine. Countries where codeine predominated, appeared to have high overall opioid prescribing, which was reversed when OMEQ was used and the contribution of ‘strong’ opioids accounted for.43
Prescribers’ understanding of OMEQ is poor.51–53 Use of OMEQ as a measure of prescribing might improve comprehension of opioid equivalence and lead to safer prescribing.
Substantial increases in opioid prescribing, with higher levels in more deprived populations, were also reported in other parts of the UK2,27 and internationally.54–57 Increased levels of prescribing in areas of high socioeconomic deprivation has been linked to greater reported pain intensity.26 However, limited evidence supports the notion that opioids are effective at reducing pain, particularly in the longer term.8,58,59 High-dose opioids (above 120 mg OMEQ) have been associated with increased levels of pain.60,61 In the context of this and previous studies,2,6,26,27 the implications of increased opioid prescribing in more deprived areas are concerning. It exposes the most vulnerable people to higher levels of medicines, which may be ineffective at best, and could cause additional health and well-being complications.11
Implications for practice
OMEQ is a useful measure of opioid utilisation in the general population and an individual basis.25 This study has demonstrated differences between assumed burden of opioid prescribing using OMEQe and prescriptions issued, which might have important clinical implications. Evaluating opioid prescribing using OMEQ would provide easily comparable data that better reflects clinical practice. Reasons for disparities in opioid burden between areas of deprivation need further investigation. Lack of availability and acceptability of non-pharmacological management and services have been suggested among reasons why prescribing is favoured.62,63 Use of OMEQ as a measure of opioid burden should be considered as a means of identifying ‘at risk’ populations and individuals, as prescription numbers reduce.
Funding
This work was supported by Pharmacy Research UK (grant reference number: PRUK-2016- PA1-A). Emma Davies’ PhD is partly supported by funding from Research Capacity Building Collaboration (RCBC Wales).
Ethical approval
This research was approved by the Information Governance Review Panel (IGRP) of the SAIL databank, based in Swansea University (SAIL identification number: 0507)
Provenance
Freely submitted; externally peer reviewed.
Acknowledgements
This study makes use of anonymised data generated by the SAIL system, which is part of the national e-health records research infrastructure for Wales. The authors would like to acknowledge all the data providers who make anonymised data available for research.
Patient consent
There was no direct patient involvement in the development and design of this study. However, the SAIL databank has members of the public who provide advice and give recommendations on safeguarding and ethical approval via a consumer panel. Panel members also provide input to the IGRP, which approves all data applications.
Competing interests
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
References
- 1.Zin CS, Chen LC, Knaggs RD. Changes in trends and pattern of strong opioid prescribing in primary care. Eur J Pain. 2014;18(9):1343–1351. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2014.496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mordecai L, Reynolds C, Donaldson LJ, de C Williams AC. Patterns of regional variation of opioid prescribing in primary care in England: a retrospective observational study. Br J Gen Pract. 2018;68(668):e225–e233. doi: 10.3399/bjgp18X695057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ruscitto A, Smith BH, Guthrie B. Changes in opioid and other analgesic use 1995-2010: repeated cross-sectional analysis of dispensed prescribing for a large geographical population in Scotland. Eur J Pain. 2015;19(1):59–66. doi: 10.1002/ejp.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Davies E, Phillips C, Rance J, Sewell B. Examining patterns in opioid prescribing for non-cancer-related pain in Wales: preliminary data from a retrospective cross-sectional study using large datasets. Br J Pain. 2019;13(3):145–158. doi: 10.1177/2049463718800737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bedson J, Chen Y, Hayward RA, et al. Trends in long-term opioid prescribing in primary care patients with musculoskeletal conditions: an observational database study. Pain. 2016;157(7):1525–1531. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Curtis HJ, Croker R, Walker AJ, et al. Opioid prescribing trends and geographical variation in England, 1998-2018: a retrospective database study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6(2):140–150. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30471-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stannard C. Where now for opioids in chronic pain? Drug Ther Bull. 2018;56(10):118–122. doi: 10.1136/dtb.2018.10.000007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Faculty of Pain Management, Royal College of Anaesthetists Opioids aware: a resource for patients and healthcare professionals to support prescribing of opioid medicines for pain. https://www.fpm.ac.uk/opioids-aware. [26 Nov 2020];
- 9.Rosenblum A, Marsch LA, Joseph H, Portenoy RK. Opioids and the treatment of chronic pain: controversies, current status, and future directions. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;16(5):405–416. doi: 10.1037/a0013628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ballantyne JC, Shin NS. Efficacy of opioids for chronic pain. Clin J Pain. 2008;24(6):469–478. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e31816b2f26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Els C, Jackson TD, Kunyk D, et al. Adverse events associated with medium- and long-term use of opioids for chronic non-cancer pain: an overview of Cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;10(10):CD012509. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012509.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lin JC, Chu LF, Stringer EA, et al. One month of oral morphine decreases gray matter volume in the right amygdala of individuals with low back pain: confirmation of previously reported magnetic resonance imaging results. Pain Med. 2016;17(8):1497–1504. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnv047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Scherrer JF, Salas J, Sullivan MD, et al. The influence of prescription opioid use duration and dose on development of treatment resistant depression. Prev Med. 2016;91:110–116. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.08.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gomes T, Mamdani MM, Dhalla IA, et al. Opioid dose and drug-related mortality in patients with nonmalignant pain. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(7):686–691. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2011.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Merrill JO, Von Korff M, Banta-Green CJ, et al. Prescribed opioid difficulties, depression and opioid dose among chronic opioid therapy patients. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2012;34(6):581–587. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2012.06.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Scherrer JF, Salas J, Copeland LA, et al. Prescription opioid duration, dose, and increased risk of depression in 3 large patient populations. Ann Fam Med. 2016;14(1):54–62. doi: 10.1370/afm.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Morasco BJ, Yarborough BJ, Smith NX, et al. Higher prescription opioid dose is associated with worse patient-reported pain outcomes and more health care utilization. J Pain. 2017;18(4):437–445. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2016.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Salas J, Scherrer JF, Schneider FD, et al. New-onset depression following stable, slow, and rapid rate of prescription opioid dose escalation. Pain. 2017;158(2):306–312. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fischer B, Murphy Y, Kurdyak P, Goldner EM. Depression — a major but neglected consequence contributing to the health toll from prescription opioids? Psychiatry Res. 2016;243:331–334. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.06.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mazereeuw G, Sullivan MD, Juurlink DN. Depression in chronic pain: might opioids be responsible? Pain. 2018;159(11):2142–2145. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ballantyne JC, LaForge KS. Opioid dependence and addiction during opioid treatment of chronic pain. Pain. 2007;129(3):235–255. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.03.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Minozzi S, Amato L, Davoli M. Development of dependence following treatment with opioid analgesics for pain relief: a systematic review. Addiction. 2013;108(4):688–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.04005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Campbell G, Nielsen S, Larance B, et al. Pharmaceutical opioid use and dependence among people living with chronic pain: associations observed within the pain and opioids in treatment (point) cohort. Pain Med. 2015;16(9):1745–1758. doi: 10.1111/pme.12773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Degenhardt L, Lintzeris N, Campbell G, et al. Experience of adjunctive cannabis use for chronic non-cancer pain: findings from the pain and opioids in treatment (point) study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015;147:144–150. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.11.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nielsen S, Gisev N, Bruno R, et al. Defined daily doses (DDD) do not accurately reflect opioid doses used in contemporary chronic pain treatment. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2017;26(5):587–591. doi: 10.1002/pds.4168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Todd A, Akhter N, Cairns J-M, et al. The pain divide: a cross-sectional analysis of chronic pain prevalence, pain intensity and opioid utilisation in England. BMJ Open. 2018;8(7):e023391. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen T-C, Chen L-C, Kerry M, Knaggs RD. Prescription opioids: Regional variation and socioeconomic status — evidence from primary care in England. Int J Drug Policy. 2019;64:87–94. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2018.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Marmot M, Bell R. Fair society, healthy lives. Public Health. 2012;126(Supp 1):S4–S10. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2012.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Office for National Statistics Deaths related to drug poisoning in England and Wales: 2018 registrations. https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarriages/deaths/bulletins/deathsrelatedtodrugpoisoninginenglandandwales/2018registrations. [26 Nov 2020];2019
- 30.Keyes KM, Cerdá M, Brady JE, et al. Understanding the rural–urban differences in nonmedical prescription opioid use and abuse in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2014;104(2):e52–e59. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Stannard CF. Pain and pain prescribing: what is in a number? Br J Anaesth. 2018;120(6):1147–1149. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Taylor S, Annand F, Burkinshaw P, et al. Dependence and withdrawal associated with some prescribed medicines: an evidence review. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/829777/PHE_PMR_report.pdf. [26 Nov 2020];2019
- 33.Torrance N, Veluchamy A, Zhou Y, et al. Trends in gabapentinoid prescribing, co-prescribing of opioids and benzodiazepines, and associated deaths in Scotland. Br J Anaesth. 2020;125(2):159–167. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2020.05.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Edwards RT, Charles JM, Thomas S, et al. A national programme budgeting and marginal analysis (PBMA) of health improvement spending across Wales: disinvestment and reinvestment across the life course. BMC Public Health. 2014;14(1):837. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Barnard H. Poverty in Wales 2018. https://www.jrf.org.uk/report/poverty-wales-2018. [26 Nov 2020];2018
- 36.Welsh Government Welsh index of multiple deprivation: 2011. https://gov.wales/welsh-index-multiple-deprivation-full-index-update-ranks-2011. [26 Nov 2020];2011
- 37.Lyons RA, Jones KH, John G, et al. The Sail databank: linking multiple health and social care datasets. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2009;9(1):3. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-9-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ford DV, Jones KH, Verplancke J-P, et al. The Sail Databank: building a national architecture for e-health research and evaluation. BMC Health Serv Res. 2009;9:157. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-9-157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Joint Formulary Committee British National Formulary. https://about.medicinescomplete.com/publication/british-national-formulary. [26 Nov 2020];2020
- 40.Datapharm Electronic medicines compendium. Up to date, approved, regulated prescribing and patient information for licensed medicines. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc. [26 Nov 2020];2020
- 41.Office for National Statistics London: ONS; 2013. 2011 census analysis — comparing rural and urban areas of England and Wales. [Google Scholar]
- 42.StatsWales Population estimates by local authority and year. https://statswales.gov.wales/Catalogue/Population-and-Migration/Population/Estimates/Local-Authority/populationestimates-by-localauthority-year. [26 Nov 2020];2020
- 43.Svendsen K, Borchgrevink P, Fredheim O, et al. Choosing the unit of measurement counts: the use of oral morphine equivalents in studies of opioid consumption is a useful addition to defined daily doses. Palliat Med. 2011;25(7):725–732. doi: 10.1177/0269216311398300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Foy R, Leaman B, McCrorie C, et al. Prescribed opioids in primary care: cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses of influence of patient and practice characteristics. BMJ Open. 2016;6(5):e010276. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Williams T, van Staa T, Puri S, Eaton S. Recent advances in the utility and use of the general practice research database as an example of a UK primary care data resource. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2012;3(2):89–99. doi: 10.1177/2042098611435911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jones KH, Ford DV, Jones C, et al. A case study of the Secure Anonymous Information Linkage (SAIL) gateway: a privacy-protecting remote access system for health-related research and evaluation. J Biomed Inform. 2014;50:196–204. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2014.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Karanges EA, Blanch B, Buckley NA, Pearson S-A. Twenty-Five years of prescription opioid use in Australia: a whole-of-population analysis using pharmaceutical claims. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;82(1):255–267. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.All Wales Medicines Strategy Group National prescribing indicators 2019–2020. https://awmsg.nhs.wales/files/national-prescribing-indicators/national-prescribing-indicators-2019-2020. [26 Nov 2020];2019
- 49.OpenPrescribing.net Opioid analgesics. https://openprescribing.net/bnf/040702. [26 Nov 2020];2020
- 50.World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology Guidelines for ATC classification and DDD assignment: 2020. https://www.whocc.no/filearchive/publications/2020_guidelines_web.pdf. [26 Nov 2020];2019
- 51.Rennick A, Atkinson T, Cimino NM, et al. Variability in opioid equivalence calculations. Pain Med. 2016;17(5):892–898. doi: 10.1111/pme.12920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Shaheen PE, Walsh D, Lasheen W, et al. Opioid equianalgesic tables: are they all equally dangerous? J Pain Symptom Manage. 2009;38(3):409–417. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2009.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Institute for Safe Medication Practices Canada Sink or swim? Helping patients and practitioners to understand opioid potencies and overdose risk. ISMP Canada Safety Bulletin. 2017;17(8):1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Joynt M, Train MK, Robbins BW, et al. The impact of neighborhood socioeconomic status and race on the prescribing of opioids in emergency departments throughout the United States. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28(12):1604–1610. doi: 10.1007/s11606-013-2516-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wagemaakers FN, Hollingworth SA, Kreijkamp-Kaspers S, et al. Opioid analgesic use in Australia and the Netherlands: a cross-country comparison. Int J Clin Pharm. 2017;39(4):874–880. doi: 10.1007/s11096-017-0492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kapoor S, Thorn BE. Healthcare use and prescription of opioids in rural residents with pain. Rural Remote Health. 2014;14(3):2879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Prunuske JP, St Hill CA, Hager KD, et al. Opioid prescribing patterns for non-malignant chronic pain for rural versus non-rural US adults: a population-based study using 2010 NAMCS data. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14(1):563. doi: 10.1186/s12913-014-0563-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Furlan AD, Sandoval JA, Mailis-Gagnon A, Tunks E. Opioids for chronic noncancer pain: a meta-analysis of effectiveness and side effects. CMAJ. 2006;174(11):1589–1594. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.051528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Chaparro LE, Furlan AD, Deshpande A, et al. Opioids compared with placebo or other treatments for chronic low back pain: an update of the Cochrane review. Spine. 2014;39(7):556–563. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Cohen SP, Christo PJ, Wang S, et al. The effect of opioid dose and treatment duration on the perception of a painful standardized clinical stimulus. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2008;33(3):199–206. doi: 10.1097/00115550-200805000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tompkins DA, Campbell CM. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia: clinically relevant or extraneous research phenomenon? Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2011;15(2):129–136. doi: 10.1007/s11916-010-0171-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Finestone HM, Juurlink DN, Power B, et al. Opioid prescribing is a surrogate for inadequate pain management resources. Can Fam Physician. 2016;62(6):465–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.McCrorie C, Closs SJ, House A, et al. Understanding long-term opioid prescribing for non-cancer pain in primary care: a qualitative study. BMC Fam Pract. 2015;16(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12875-015-0335-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Pain Management Centre, Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Opioid calculator for calculation of oral morphine equivalent daily dose (MED) in mg/day. https://www.ouh.nhs.uk/services/referrals/pain/documents/opioid-calculator.xlsx. [26 Nov 2020];2020