Figure 6.
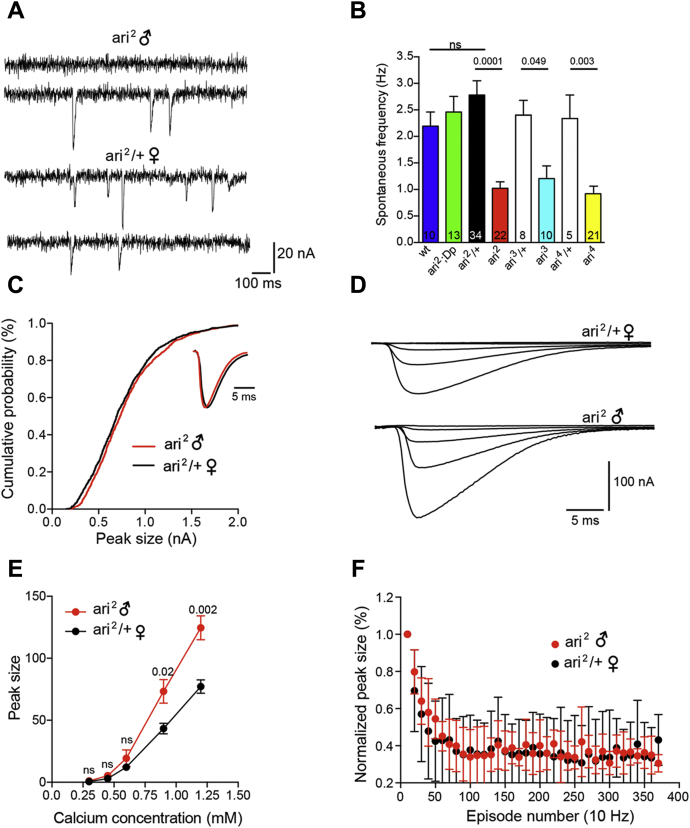
Synaptic release is affected in ari-1 mutants.A, mEJC frequency in ari-1 mutants is reduced. Representative traces from a spontaneous mEJCs recording. Events were captured under TEVC (Vh = –80 mV) from larval muscle 6 fibers in ari2 mutant male (top) and in heterozygous ari2/+ female siblings (bottom). B, quantification of the effects over spontaneous release. mEJC frequency (mean ± SEM) was calculated from the following larvae strains; (wt), ari2♂ covered by the duplication Dp(1;3)JC153 (ari2;Dp), heterozygous ari2 female siblings (ari2/+ ♀), ari2♂ and two additional ari alleles (ari3 and ari4), and their respective heterozygous females. Student's t test. Note the consistent reduction of mEJC frequency across all mutant genotypes with respect to the sibling female controls. ari2 is a C150Y mutation in the first R motif of the RBR domain; ari3 is a C309Y mutation in the second R motif; and ari4 is a point mutation that generates a STOP codon at amino acid 91. C, neither size nor mEJC time course is affected in ari2 animals. Cumulative probability curve of mEJC amplitudes for ari2/+ ♀ (black) and ari2♂ (red) larvae (n = 7 larvae). Inset: average representative mEJC traces from ari2♂ mutant superimposed to that of ari2/+ ♀. Traces were scaled up to the maximum peak value. D, representative traces of evoked transmitter release recorded under TEVC (Vh = −80 mV), at increasing extracellular Ca2+ concentrations (from 0.3 to 1.2 mM), recorded from sibling ari2/+ ♀ and ari2♂ larvae. E, quantification of Ca2+ dependence of evoked release. Maximal EJC response was plotted versus the extracellular calcium concentration for ari2♂ compared with ari2/+ ♀ (n = 6 for all genotypes; one-way ANOVA post hoc: Student's t test). F, quantification of EJC trains in response to a 10 Hz stimulation. Peak size was normalized to their initial response. Average of six different experiments from ari2♂ and ari2/+ ♀ larvae.