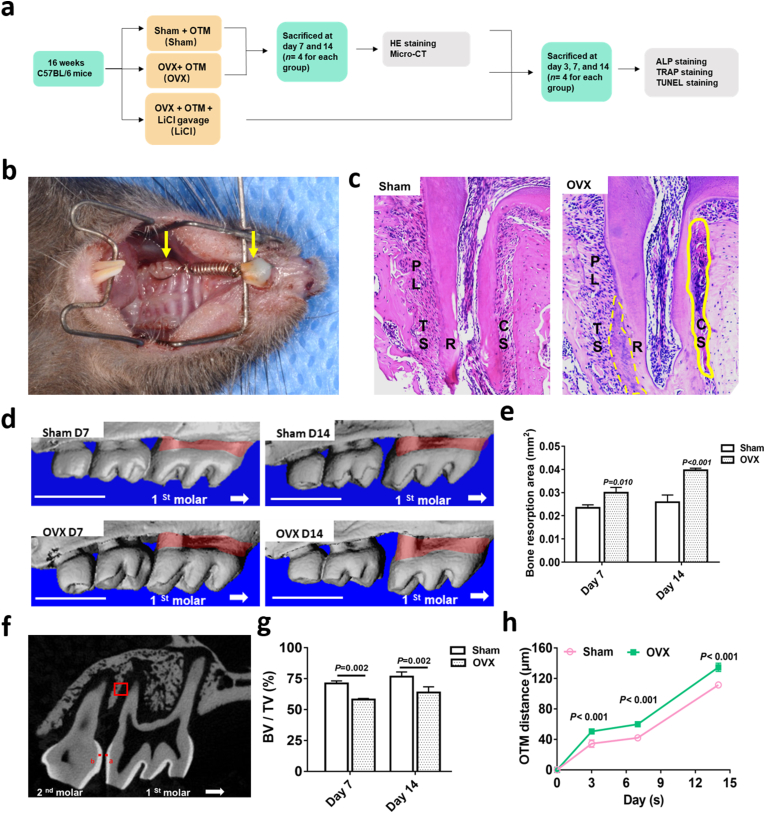
Fig. 2.
Ovariectomy increased OTM distance and bone resorption in mice. a, a flowchart of the in vivo study. b, Orthodontic tooth movement (OTM) model. The left yellow arrow indicated the right upper first molar. The right yellow arrow indicated the upper incisor. c, Representative images of H&E staining of tooth movement on day 14 in the sham and OVX mice. The solid yellow box at the pressure side indicated hyaline change. The dotted yellow box at the tension side indicated hypercementosis. TS, the tension side; CS, the compressive side; PL, periodontal ligament; R; root. d, Three-dimensional reconstruction of the maxilla samples from the sham and OVX groups. Vertical bone resorption was indicated by the red-marked area. Scale bar: 1 mm e, Quantification of vertical bone resorption in different groups. f, Sagittal view of landmark point locations and method for the measurement of OTM distance in micro-computed tomography images. Landmark points a and b were indicated. The red box indicated ROI in alveolar bone. g, The value of BV/TV around the apical part of the distal buccal root of the maxillary right first molar. h, The OTM distance in the sham and OVX groups. Data represent means ± S. D (n = 3). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)