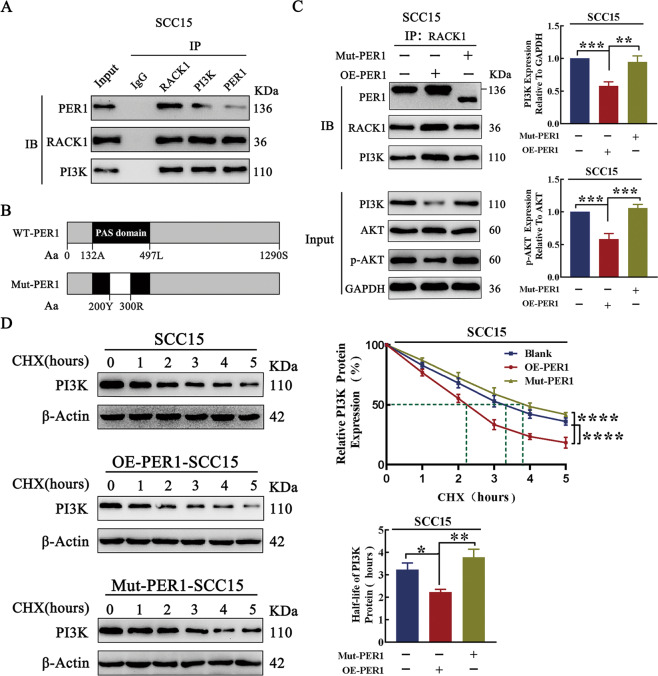
Fig. 6. Regulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway via the PER1/RACK1/PI3K complex.
A The Co-IP results showed that PER1 interacted with RACK1 and PI3K to form the PER1/RACK1/PI3K complex. B The amino acid sequences of wild-type and mutant PER1 (the blank box represents the amino acid sequence of the deletion mutant). A stands for alanine, L for leucine, S for serine, Y for tyrosine, and R for arginine. C The Co-IP and western blot results showed that, in OE-PER1-SCC15 cells, the abundance of the PER1/RACK1/PI3K complex was significantly increased but the intracellular protein levels of total PI3K and p-AKT were significantly decreased, while in Mut-PER1-SCC15 cells, the increase in the abundance of the PER1/RACK1/PI3K complex and the decreases in the intracellular protein levels of total PI3K and p-AKT were significantly reversed. D The CHX chase experiment showed that the half-life of the PI3K protein in OE-PER1-SCC15 cells was significantly decreased, while the decrease in the half-life of the PI3K protein was significantly reversed in Mut-PER1-SCC15 cells. All data are from three independent experiments. The data are presented as the mean ± SD values (n ≥ 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.