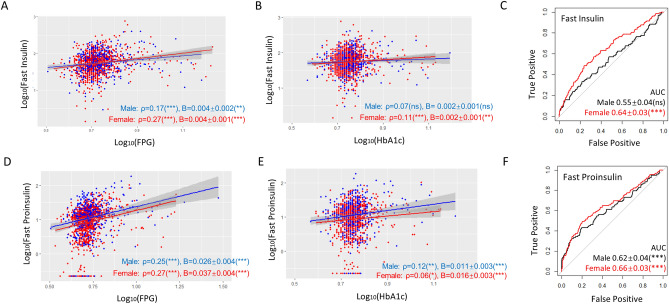
Figure 4.
Fasting insulin and proinsulin levels predict T2D better in women than in men. (A,B) Fasting insulin levels associate with and affect FPG and HbA1c stronger in women than in men as judge from Spearman’s ρ and regression coefficient B. P values, regression constant can be found in Tables S2 and S3. (C) Fasting insulin is a stronger T2D predictor for women as judged by ROC-AUC values. (D) Fasting proinsulin levels associate with and affect FPG and HbA1c stronger in women than in men. (E) Fasting proinsulin levels are weakly associated with HbA1c in women. (F) Fasting proinsulin is a stronger T2D predictor for women as judged by ROC-AUC values. AUC area under the curve, ns not significant, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.