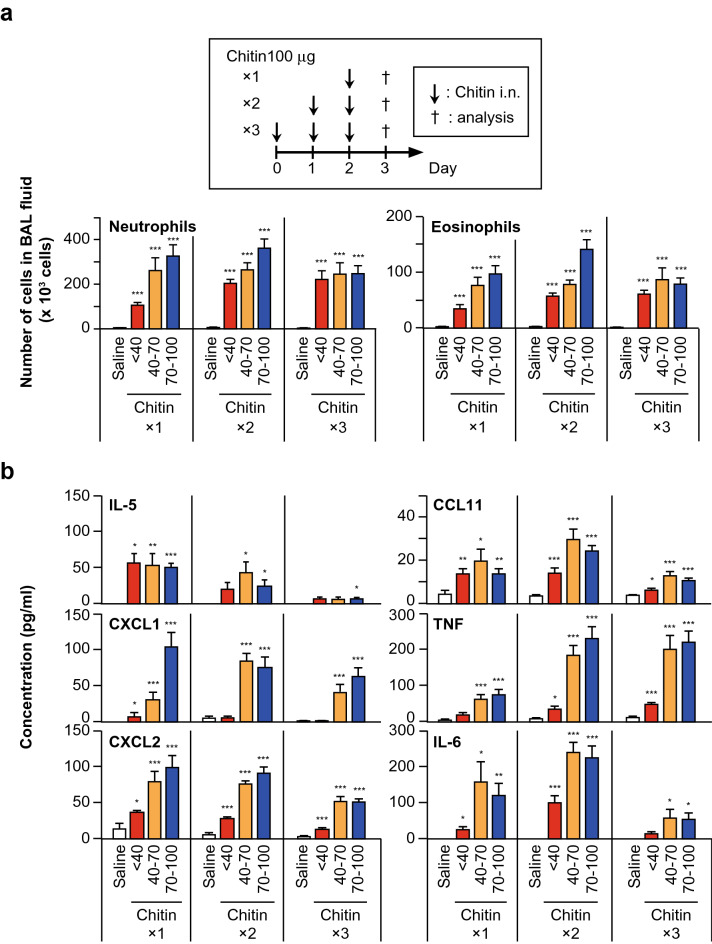
Figure 2.
Induction of robust airway inflammation in mice by a single inhalation of chitin. C57BL/6 J-wild-type mice were intranasally treated one, two or three times with 100 μg of chitin (small: < 40 μm; medium: 40–70 μm; large: 70–100 μm) suspended in saline or with saline alone. Twenty-four hours after the last inhalation of chitin or saline alone, BAL fluids and lungs were collected. (a) Each type of cell (eosinophils, neutrophils) in the BAL fluids were counted. (b) The levels of cytokines and chemokines in the BAL fluids were measured by ELISA. Data from 2 independent experiments were pooled and shown as the mean + SE (n = 10). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005 vs. saline alone (= 0 μg of chitin).