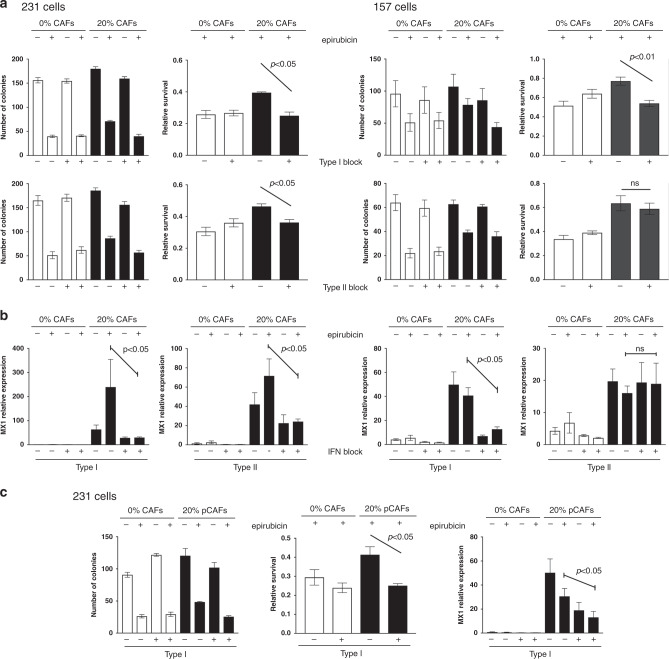
Fig. 6. Blocking antibodies inhibit CAF-induced chemoprotection.
a, b MDA-MB-231-GFP/luc (left) or MDA-MB-157 (right) cells were cultured alone, or with breast CAFs or CAF-GFP cells, respectively. Cultures were treated with type I (1 μg/ml) or type II (5 μg/ml) interferon-signalling blocking antibodies or appropriate isotype controls for 24 h. Cultures were then treated with 10 nM (MDA-MB-231 cells) or 25 nM (MDA-MB-157 cells) epirubicin or vehicle control, and were redosed with antibodies for a further 24 h. Epithelial cells were then collected by FACS. a Clonogenic survival was determined. Data are presented as colony counts or relative survival after epirubicin (colony counts relative to untreated). b Relative expression of the marker of IFN-signalling activity MX1 was determined. c MDA-MB-231-GFP/luc cells were cultured alone, or with primary breast CAFs and were treated with antibodies and epirubicin/control exactly as above. Clonogenic survival was determined (left): data are presented as colony counts or relative survival after epirubicin (colony counts relative to untreated). Relative expression of the marker of IFN-signalling activity MX1 was also determined (right). a, b, c Data represent means (±SE) of three independent experimental repeats. Two-tailed Mann–Whitney U tests were carried out and selected differences are shown (ns not significant).