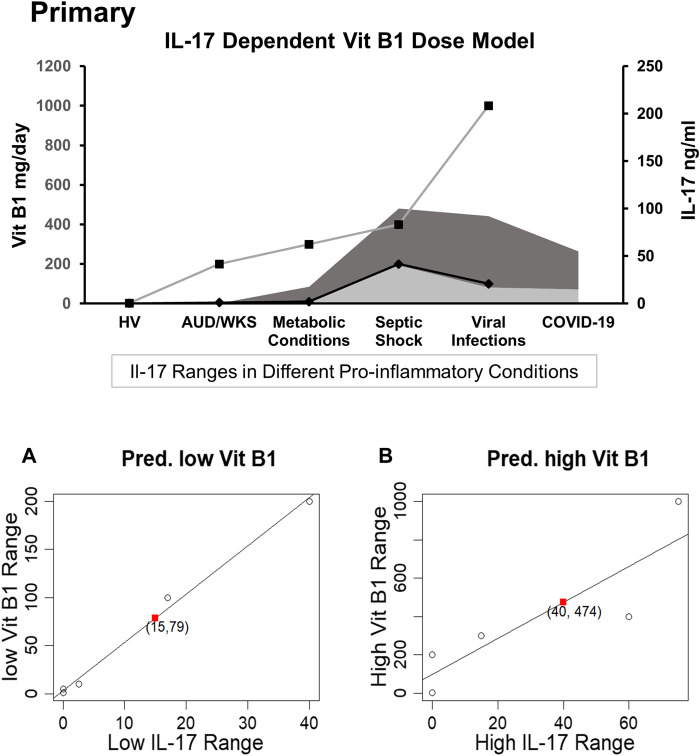
FIGURE 2.
PRIMARY: A dose titration by disease and proinflammatory Th17 status model of thiamine administration with parallel representation of Th17 proinflammatory response in various groups including healthy volunteers and disease groups with pro-inflammatory response. (A) Linear regression model is predictive for the relation between the low dose thiamine (Vit B1) range vs. low IL-17 ranges based on known observed pairs from different patients; lower range of vit B1 dose (79 mg/daily) corresponding to lower range of IL-17 (15 ng/ml) in the COVID-19 patients. Dark grey shade depicts higher IL-17 response and lighter grey shade shows lower IL-17 response in various proinflammatory conditions. (B) Linear regression shows the predictive model for the relation between a higher range of Vit B1 dose vs. a higher range of IL-17 levels, derived from the known observed pairs from different patients; higher range of Vit B1 dose (474 mg/daily) corresponding to higher range of IL-17 (40 ng/ml) reported in COVID-19 patients. High Range Thiamine Dose: Left Y-axis (primary). Low Range Thiamine Dose, Low Range IL-17 levels, and High range IL-17 levels: Right Y-axis (Secondary).