Figure 1.
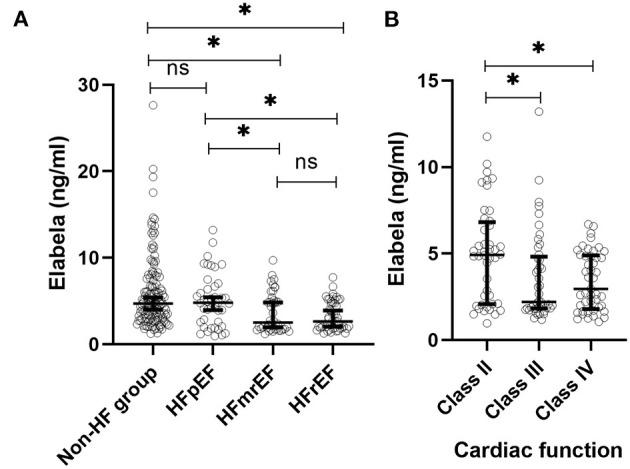
Plasma Elabela levels in hypertensive patients with different types of HF. (A) The mean plasma Elabela level of the non-HF group were similar with that of HFpEF group. Plasma Elabela levels of patients with HFrEF were similar with that of HFmrEF. Furthmore, patients without HF had a higher mean plasma level of Elabela compared with patients with HFrEF and HFmrEF separately [4.7 (3.0, 7.4) vs. 2.6 (1.9, 4.9) ng/ml, P = 0.01 and 4.7 (3.0, 7.4) vs. 2.7 (1.8, 5.4) ng/ml, P < 0.001 separately]. Importanly, patients with HFpEF had higher plasma levels of Elabela than patients with HFrEF and HFmrEF separately [4.8 (2.4, 6.8) vs. 2.6 (1.9, 4.9) ng/ml, P = 0.010 and 4.8 (2.4, 6.8) vs. 2.7 (1.8, 5.4) ng/ml, P = 0.037 separately]. (B) There were no difference of plasma Elabela levels between HF patients with NYHA class III and IV; Plasma Elabela levels were significantly higher in HF patients with NYHA class II than those with NYHA class III and class IV separately [4.9 (2.1, 6.8) vs. 2.2 (1.8, 4.8), P = 0.007 and 4.9 (2.1, 6.8) vs. 3.0 (1.8, 4.9) ng/ml, P = 0.011 separately]. ELA, Elabela; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; HFmrEF, heart failure with middle-range fraction; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; NYHA, New York Heart Association.
