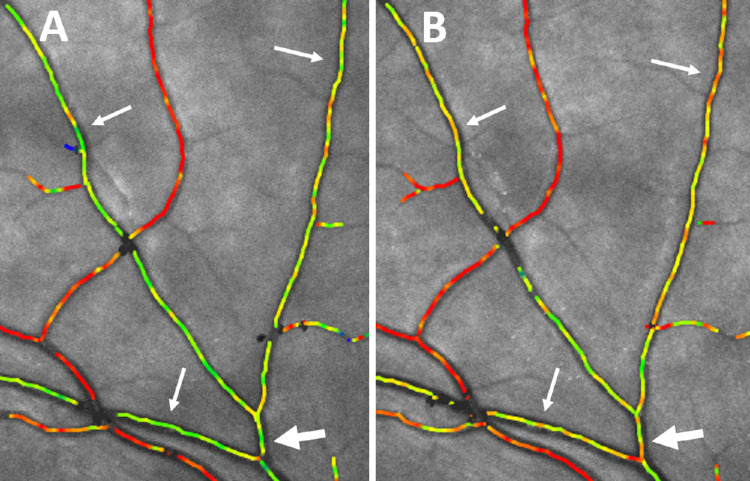
Figure 3.
High magnification of oximetry images centered on the upper temporal arcades. (A) Before isometric exercise. The arrows point to venular segments draining the retinal periphery marked in green. The large arrow points to the segment with a diameter approximately 100 µm from which the saturation was measured to be 66%. (B) The same area 30 seconds after starting isometric exercise that increased the mean arterial blood pressure by 11.8 mm Hg. The color of the venules pointed to by the arrows can be seen to have become more yellowish, and the oxygen saturation pointed at with the large arrow had increased to 73%.