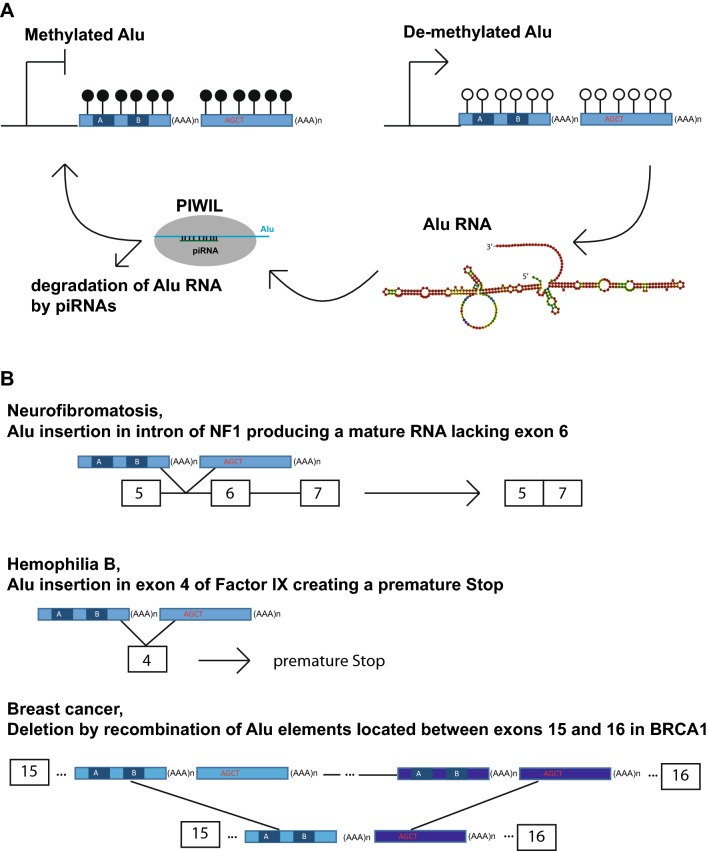
Fig. 3.
Mechanisms controlling Alu activities and examples of Alu in Human diseases. a Epigenetic and post-transcriptional mechanisms controlling Alu activity. DNA methylation prevent Alu transcription. In case of de-methylated Alu such as during reprograming, Alu RNAs could be post-transcriptionally controlled by P-element-induced wimpy testis (PIWI)-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). The piRNAs control retro-transposition by destroying the RNA encoded by Alu within the piRNA-induced silencing complexes (piRISC). In addition, piRNAs and may also help for de novo DNA methylation of Alu. b Role of Alu is developmental diseases. Three examples that are discussed in the text are schematized. First, an Alu insertion within an intron causing neurofibromatosis. Second, an Alu insertion within an exon causing Hemophilia. Third, rearrangement in an Alu rich region of BRCA1 important for breast cancers