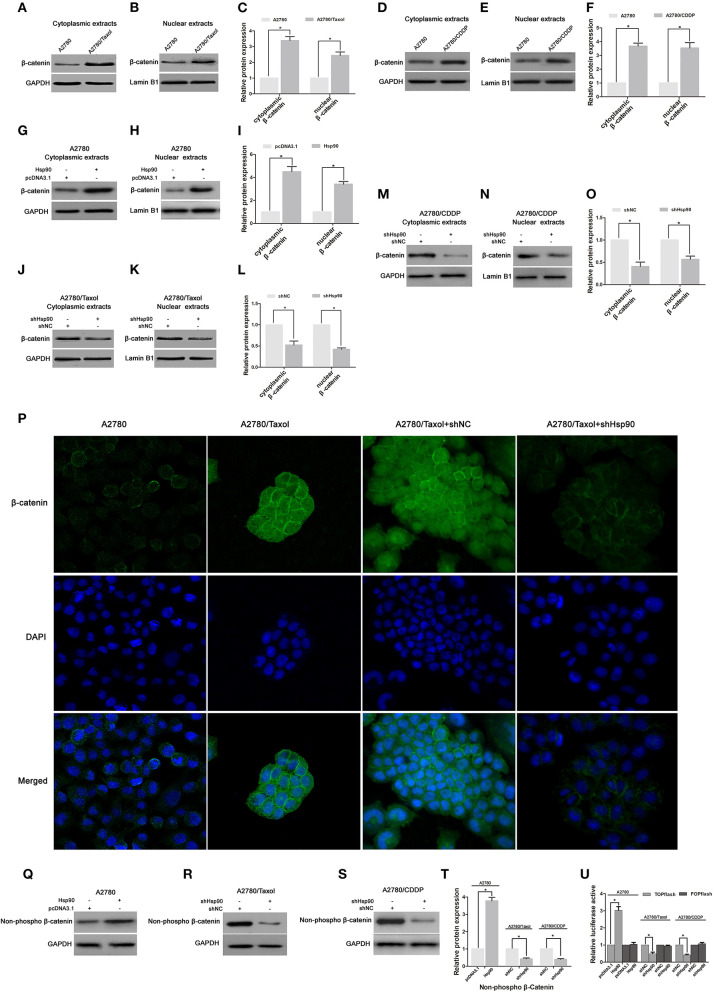
Figure 6.
The effect of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) on nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity of β-catenin. Respective western blots and relative quantitation for cytoplasmic and nuclear β-catenin in A2780, A2780/Taxol, and A2780/CDDP cells (A–F), A2780 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-Hsp90 for 72 h (G–I), A2780/Taxol and A2780/CDDP cells transfected with shNC or shHsp90 for 72 h (J–O). (P) The subcellular localization of β-catenin was analyzed using immunofluorescence staining in A2780, A2780/Taxol, and A2780/Taxol cells transfected with shNC or shHsp90 for 72 h. Green, β-catenin; blue, nuclear DNA. Respective western blots and relative quantitation for non-phospho (active) β-catenin in A2780 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-Hsp90 for 72 h, A2780/Taxol and A2780/CDDP cells transfected with shNC or shHsp90 for 72 h cells (Q–T). (U) Dual-luciferase reporter assay for TOPflash and FOPflash luciferase activity in A2780 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-Hsp90 for 48 h, A2780/Taxol and A2780/CDDP cells transfected with shNC or shHsp90 for 48 h. The relative luciferase activity was normalized against Renilla reporter pRL-SV40 activity. The results of western blotting were analyzed using ImageJ (mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments). *P < 0.05.