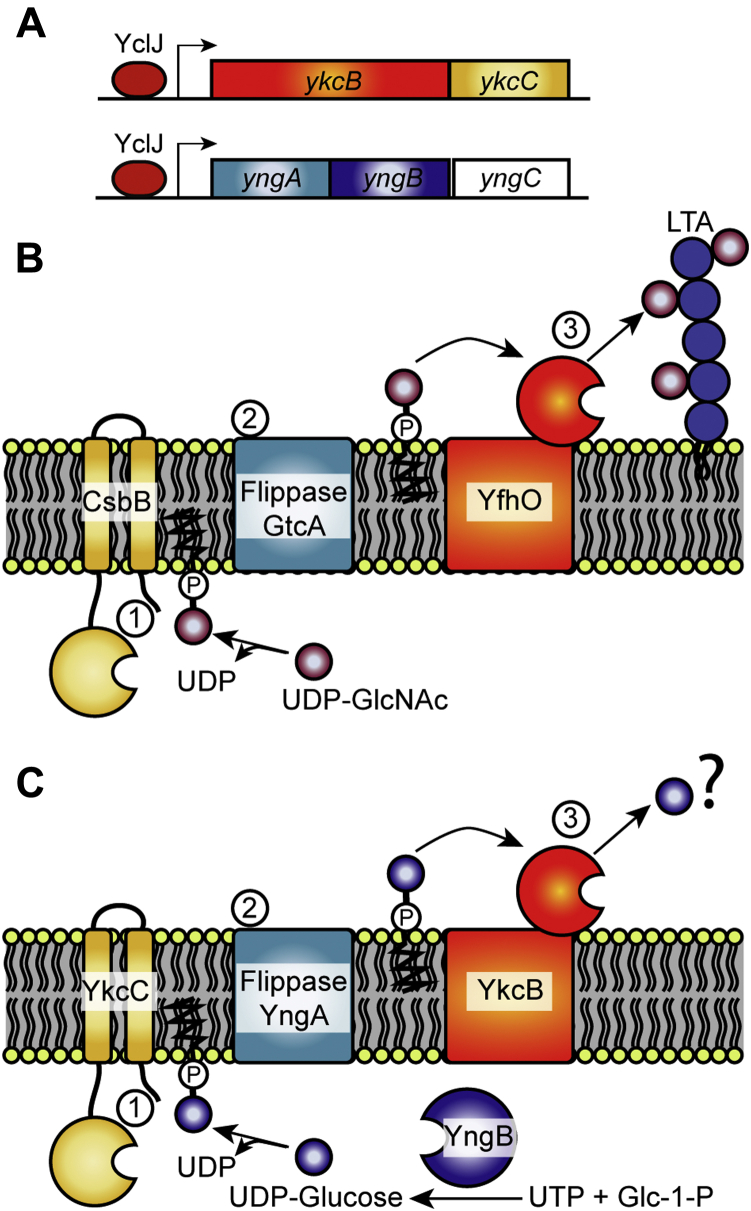
Figure 8.
Proposed glycosylation pathway involving the UGPase YngB and the YkcC-YngA-YkcB multicomponent transmembrane glycosylation system.A, the transcription factor YclJ activates the transcription of genes belonging to the ykcBC and yngABC operons. B, the Bacillus subtilis LTA glycosylation model requires CsbB, GtcA, and YfhO for the transfer of GlcNAc onto the LTA. The glycosyltransferase CsbB produces C55-P-GlcNAc, which is subsequently transported across the membrane by GtcA, and the GlcNAc is finally attached to the LTA polymer on the outside of the cell by the multimembrane–spanning GT-C-fold glycosyltransferase YfhO. C, proposed glycosylation pathway leading under anaerobic growth conditions to the transfer of glucose onto an uncharacterized target in the cell envelope. As shown in this study, YngB is a functional UGPase that can produce UDP-glucose and we hypothesize that the predicted glycosyltransferase YkcC produces C55-P-glucose, which is transported across the membrane by YngA. The glucose residue is then transferred by the predicted multimembrane spanning GT-C-fold glycosyltransferase YkcB to an unknown target within the bacterial cell envelope. Panel B was adapted from a model figure presented in the studies by Rismondo et al., 2018 (19) and Rismondo et al., 2020 (20). C55-P, undecaprenyl phosphate; LTA, lipoteichoic acid.