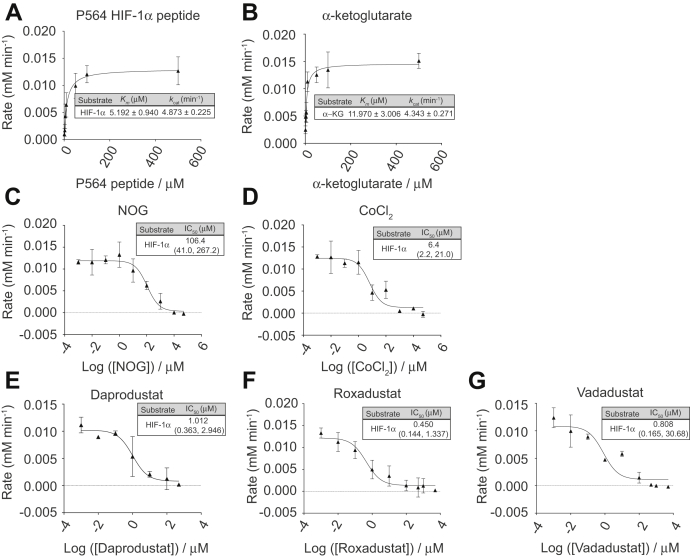
Figure 5.
Characterizing kinetic parameters of PHD2 with and without inhibitors using the 2,4-DNPH α-KG assay.A, increasing concentrations of HIF-1α peptide (P564) were added to saturating concentrations of all other reagents and 3 μM PHD2. B, increasing concentrations of α-ketoglutarate were added to 100 μM of peptide substrate and 3 μM of PHD2. C, dose response curve of N-oxalylglycine (NOG) generated by adding increasing concentrations of NOG to 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate, 100 μM HIF peptide, and 3 μM of PHD2. D, dose–response curve of cobalt (II) chloride generated by adding increasing concentrations of CoCl2 to 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate, 100 μM HIF peptide, 3 μM of PHD2. E, dose–response curve of Daprodustat generated by adding increasing concentrations of Daprodustat to 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate, 100 μM HIF peptide, and 3 μM of PHD2. F, dose–response curve of Roxadustat generated by adding increasing concentrations of Roxadustat to 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate, 100 μM HIF peptide, 3 μM of PHD2. G, dose–response curve of Vadadustat generated by adding increasing concentrations of Vadadustat to 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate, 100 μM HIF peptide, and 3 μM of PHD2. Plotted data represent three independent replicates. Number range in brackets refers to 95% confidence interval returned by Prism 8.0. α-KG, α-ketoglutarate.