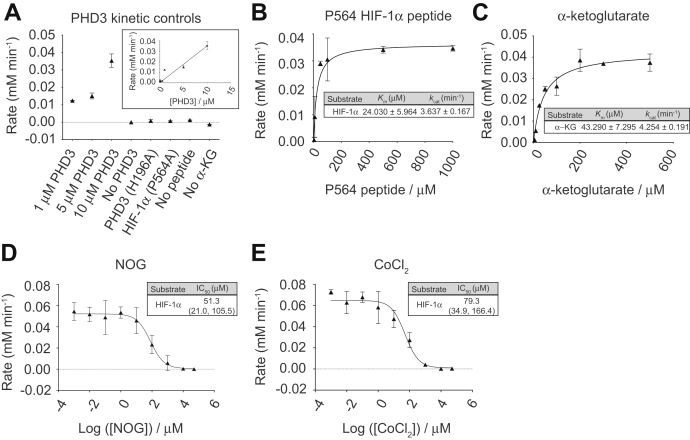
Figure 6.
Characterizing kinetic parameters of PHD3 with and without inhibitors using the 2,4-DNPH α-KG assay.A, increasing concentrations of PHD3 were added to 100 μM P564 peptide and 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate. For all negative controls, 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate, 100 μM P564 peptide, and 10 μM of PHD3 were used unless otherwise indicated. Inset shows the relationship between increasing PHD3 concentration and initial reaction rate. B, increasing concentrations of HIF-1α peptide (P564) were added to saturating concentrations of all other reagents. C, increasing concentrations of α-ketoglutarate were added to 100 μM peptide substrate and 10 μM of PHD3. D, dose–response curve of N-oxalylglycine (NOG) generated by adding increasing concentrations of NOG to 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate, 100 μM HIF peptide, and 10 μM of PHD3. E, dose–response curve of cobalt (II) chloride generated by adding increasing concentrations of CoCl2 to 0.5 mM α-ketoglutarate, 100 μM HIF peptide, and 10 μM of PHD3. NOG was chosen as a representative competitive inhibitor with respect to α-ketoglutarate, while CoCl2 was chosen as a competitive inhibitor of iron (II). Plotted data represent three independent replicates. Number range in brackets refers to 95% confidence interval returned by Prism 8.0. α-KG, α-ketoglutarate.