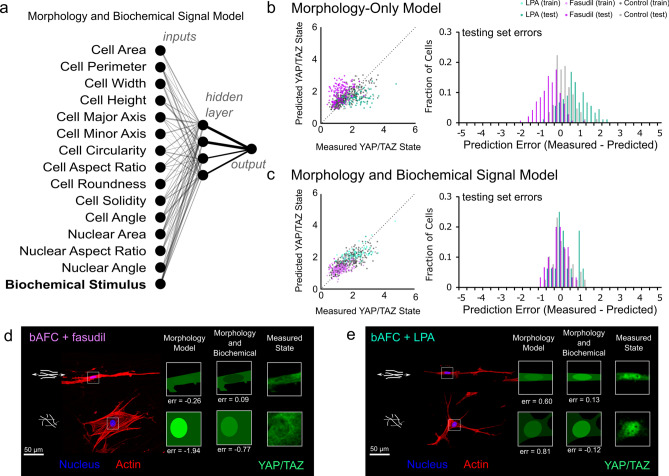
Figure 3.
(a) To account for the role that biochemical signaling can play in YAP/TAZ localization, a neural network was constructed that incorporates cell and nuclear morphology in addition to information on biochemical signaling. Line thicknesses correspond to connection weights. (b) Using a morphology-only neural network provides either over (fasudil, ROCK inhibition) or under (LPA, rhoA activation) predictions of YAP/TAZ state. (c) Incorporating biochemical signaling into the model increases model accuracy with no loss of predictability for control group cells. Example cells from the (d) Fasudil and (e) LPA groups along with visual depictions of the model predictions for both models (new model: nLPA-train = 73, nLPA-test = 16, nFasudil-train = 112, nFasudil-test = 30, ncontrol-train = 299, ncontrol-test = 39 cells).