Figure 2. Glia influence adult neurogenesis and synaptic connections formed by new neurons.
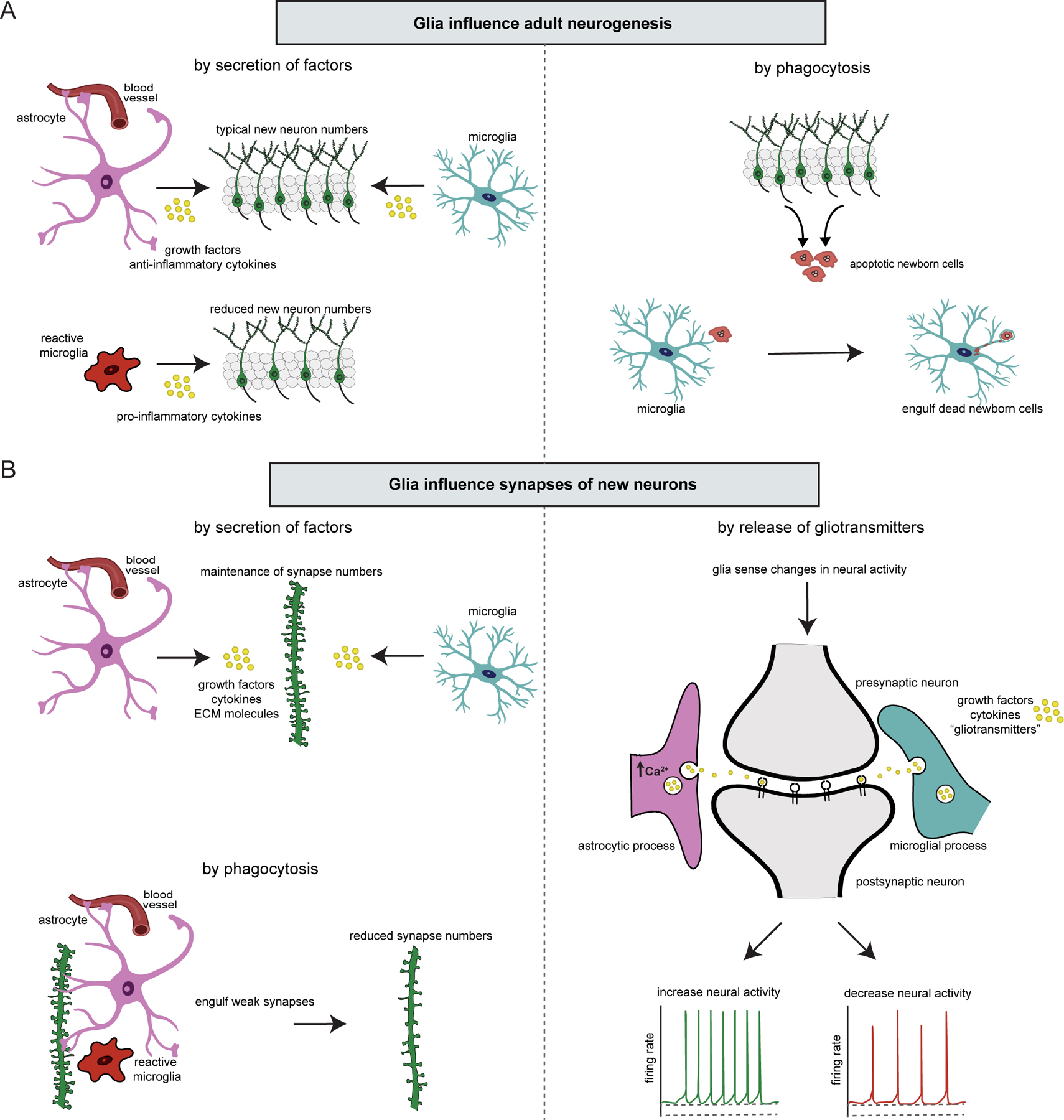
(A) Mechanisms of glial influences on adult neurogenesis. Through their secretion of growth factors and anti-inflammatory cytokines, astrocytes and microglia promote adult neurogenesis. Under pathological conditions, reactive microglia produce inflammatory cytokines that impair adult neurogenesis. Microglia also participate in adult neurogenesis by phagocytosing new neurons after they have died. (B) Mechanisms of glial influence on new neuron synapses. Astrocytes and microglia participate in regulating synapse number by secreting growth factors, cytokines, and ECM molecules. Astrocytes and microglia also shape neural circuits by engulfing weak synapses through phagocytosis. Glia modulate synaptic transmission by sensing changes in synaptic activity and releasing growth factors, cytokines, and/or gliotransmitters which, in turn, increase or decrease neural activity.
