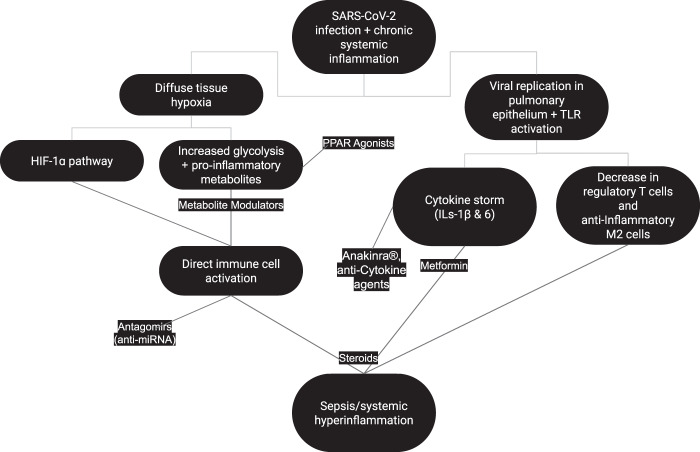
Fig. 1. Pathophysiologic changes in patients with COVID-19 and metabolic dysfunction and potential therapeutic agents.
This graph depicts the mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to hyperimmune response and sepsis in patients with metabolic dysfunction as well as potential therapeutic molcules with their targets. Diffuse tissue hypoxia and viral replication in the pulmonary epithelium along with TLR activation result in immune cell activation, cytokine release and immunomodulation. SARS-CoV-2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, IL interleukin, TLR toll-like receptor, HIF hypoxia-inducible factor, PPAR peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.