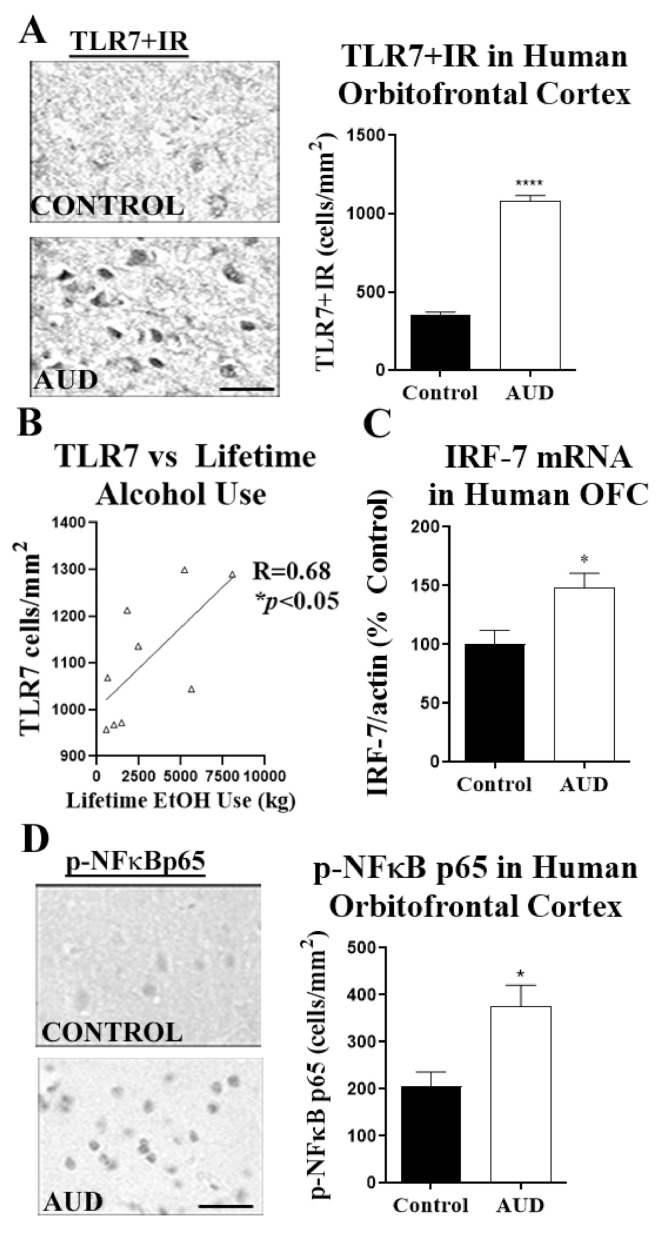
Figure 3.
TLR7 protein expression is increased in human AUD OFC and correlates with lifetime consumption of alcohol. (A) TLR7+ cell numbers in the OFC were assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC). A representative image shows a robust increase in TLR7+IR in OFC. TLR7 immunoreactive (+IR) cell counts in OFC were increased by 3-fold in humans with AUD (1079.1 ± 38.3 vs. 354.2 ± 19.6 +IR cells/mm2, **** p < 0.0001). Scale bar = 10 µm (B) TLR7+IR cell numbers from AUD subjects were positively correlated with lifetime consumption of alcohol (EtOH). R = 0.68, * p < 0.05. (C) Increased expression of the TLR7-associated transcription factor interferon regulatory factor-7 (IRF7) in postmortem human AUD OFC. (D) Levels of active phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell p65 subunit (p-NFκB p65) were measured by IHC. A representative image of p-NFκB p65+IR shows a clear increase in immunoreactive cells in AUD OFC. p-NFκB p65 was increased by 80% (376.3 ± 44.2 vs. 205.2 ± 31.2 +IR cells/mm2, * p < 0.05). n = 9–10 per group, paired t-tests.