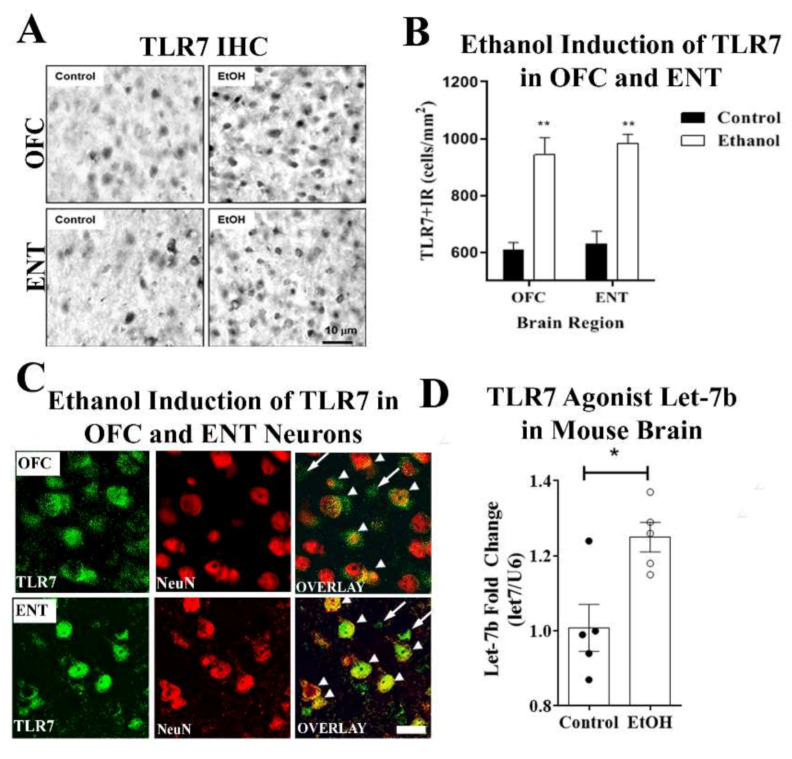
Figure 4.
Binge ethanol induces TLR7 protein and miRNA let-7b in mouse cortex. (A) C57BL/6 mice were treated with ethanol (5 g/kg, i.g.) once daily for 10 days. Mice were sacrificed 24 h after the last administration and assessed for TLR7 expression in the orbitofrontal (OFC) and entorhinal (ENT) cortices. Representative images of TLR7+IR cells in the OFC and ENT of control and ethanol-treated mouse brain regions. Scale bar = 10 µm. (B) Ethanol increased the number of TLR7 immunoreactive (+IR) cells in the OFC and ENT by 1.55- and 1.56-fold, respectively. ** p < 0.01, n = 8 OFC and n = 10 ENT per group. (C) Ethanol induction of TLR7 was observed in neurons (arrowheads) as well as in glia (long arrows) in OFC and ENT. Double immunofluorescent confocal images from ENT of a representative ethanol-treated subject. Scale bar = 20 µm. (D) C57BL/6 mice were treated with ethanol (5 g/kg, i.g.) once daily for 10 days. Mice were sacrificed 24 h after the last administration and assessed for miRNA let-7b expression and innate immune gene induction by RT-PCR as in Methods. Binge ethanol caused a 25% increase in expression of the endogenous TLR7 agonist miRNA let-7b. * p < 0.05.