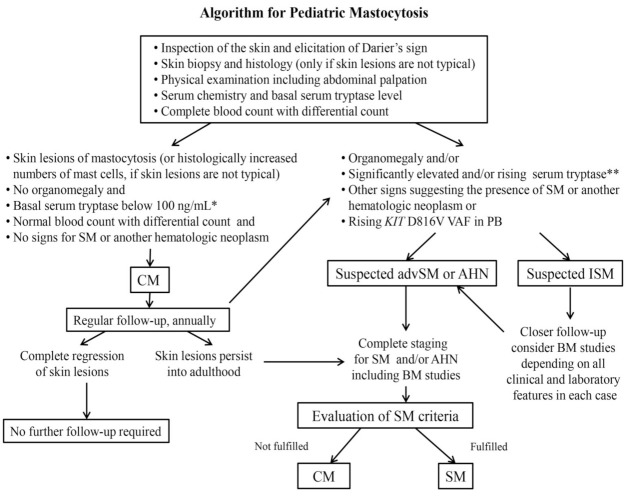
Figure 2.
Diagnostic algorithm for Pediatric Mastocytosis. In most pediatric patients with skin lesions, no signs and symptoms indicative of the presence of SM or another systemic hematologic neoplasm is found in initial investigations so that the final diagnosis is CM (left part of the algorithm). In these patients no BM investigations is performed unless the skin lesions persist into adulthood. In a few pediatric patients, however, blood count abnormalities, organomegaly and/or other findings suggest the presence of SM or another hematologic malignancy (right part of the algorithm). Depending on the abnormalities detected, these patients are more closely followed (suspected ISM) or undergo a complete staging including BM studies. Abbreviations: CM—cutaneous mastocytosis; SM—systemic mastocytosis; ISM—indolent SM; advSM—advanced SM; AHN—associated hematologic (non-mast cell) neoplasm; PB—peripheral blood; VAF—variant allele frequency; BM—bone marrow; * elevated serum tryptase level (20–100 ng/mL) should be assessed in correlation with the intensity of skin involvement and in the context of a known hereditary alpha tryptasemia; ** significantly elevated serum tryptase level is not in itself the indication for performing BM studies.