Figure 1.
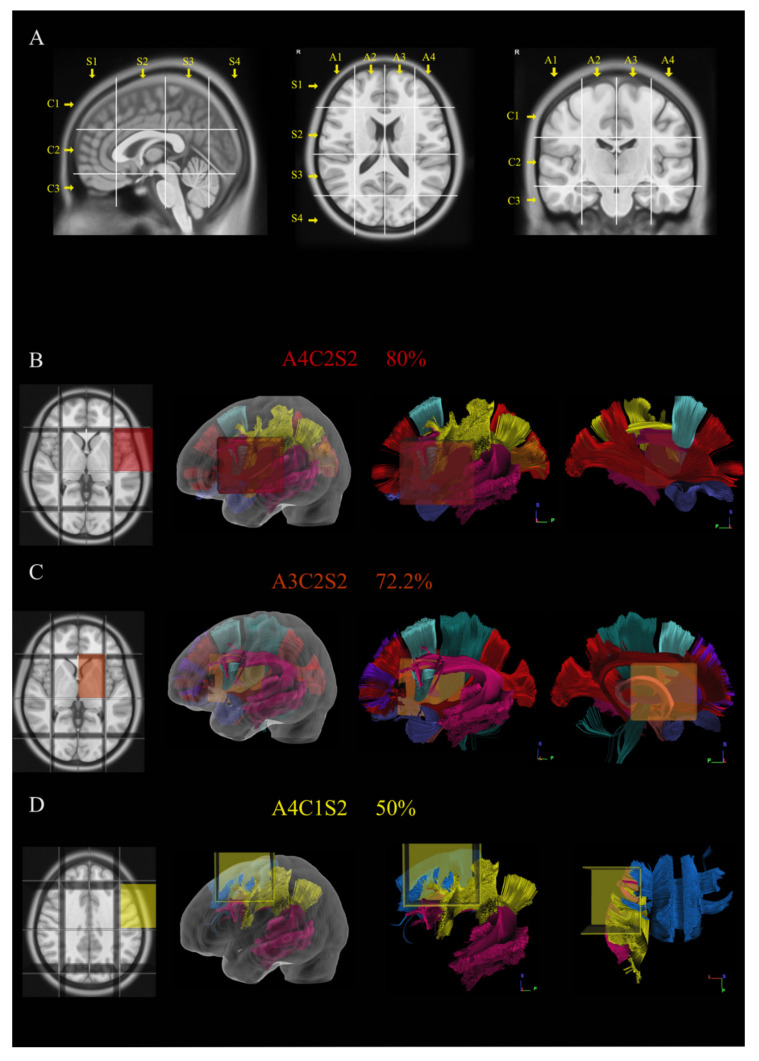
The picture shows in (A) the construction and use of Brain-Grid system in MNI space. Three sagittal lines cross the anterior insular point (the most anterior landmark of the insular sulcus), the posterior insular point and the temporo-occipital junction (between the posterior portion of the fusiform gyrus and the inferior occipital sulcus more basally on the axial plane). These lines segment the whole brain into four grid voxels labeled with the first coordinate S (from sagittal line). The S1 voxel is the pre-insular/prefrontal portion of both hemispheres. The S2 is enclosed within the anterior insular point and posterior insular point (landmark for the second sagittal line). The S3 includes the retro-insular region and the parietal lobe, and the S4 includes primarily the occipital lobe and the border with the parieto-occipital sulcus. On the coronal plane, two parallel lines cross the inferior insular point (the lowest limit of the insular sulcus), the floor of the third ventricle and the mammillary bodies, while the second line passes through the cistern/space between the Cingular gyrus and the callosal body in the midline. Three voxels are created and named after the coordinate C (from coronal plane) with C1, which is the supra callosal; C2 between the corpus callosum and the mammillary bodies; and C3, which includes the region of temporal lobe, occipital lobes and brainstem/cerebellum under the mammillary bodies. On the axial slices, the middle frontal sulcus bilaterally and the midline are chosen as three landmarks for three parallel lines. In this way, four longitudinal segments are created, termed A1–A4, from the right lateral side to the left lateral side. In total, 48 Brain-Grid voxels are created by the intersection of three sagittal lines, two coronal lines and three axial lines. (B–D) Three-dimensional (3D) reconstructions of the three most infiltrated BG voxels and the reconstruction of white matter bundles according to the BG atlas [24]: (B) A4C2S2 was infiltrated in 80% of the cases in our population. From the right to the left: position of the BG-voxel on axial T1MR sequence with morphological details; 3D glass left cerebral hemisphere with the position of the BG voxel; and the 3D reconstruction of the major white matter bundles included in the BG voxel. The glass hemisphere has been removed to show the BG voxel only with the white matter bundles from lateral sagittal view of the left hemisphere. The voxel included fibers of the indirect segment of the superior longitudinal fasciculus (hSLF; in yellow), arcuate fasciculus (AF; pink); frontal aslant tract (FAT; turquoise), anterior temporal termination of the middle longitudinal fasciculus (MdLF; orange), uncinate fasciculus (UF; orchid) and anterior termination of the inferior occipito frontal fasciculus (IFOF; red). The last image shows the reconstruction of the same voxel from the medial sagittal perspective. (C) A3C2S2 was infiltrated in 72.2% of the cases in our population. From the right to the left: position of the BG-voxel on axial T1MR sequence with morphological details; 3D glass left cerebral hemisphere with the position of the BG voxel; and the 3D reconstruction of the major white matter bundles included in the BG voxel. The glass hemisphere has been removed to show the BG-voxel only with the white matter bundles from lateral sagittal view of the left hemisphere. The voxel included fibers of AF (pink), FAT (turquoise), UF (orchid) and IFOF (red). The last image shows the reconstruction of the same voxel from the medial sagittal perspective to show the involvement of anterior thalamic radiation (ATR; grape), fornix (Fo; salmon), cingulum (Ci; cayenne) and Cortico-spinal tract (CST; teal). (D) A4C1S2 was infiltrated in 50% of the cases in our population. From the right to the left: position of the BG-voxel on axial T1MR sequence with morphological details; 3D glass left cerebral hemisphere with the position of the BG voxel; and the 3D reconstruction of the major white matter bundles included in the BG voxel. The glass hemisphere has been removed to show the BG-voxel only with the white matter bundles from lateral sagittal view of the left hemisphere. The voxel included fibers of hSLF (yellow), AF (pink) and fibers from the body of the corpus callosum (CCb; aqua). The last image shows the reconstruction of the same voxel from the dorsal perspective.