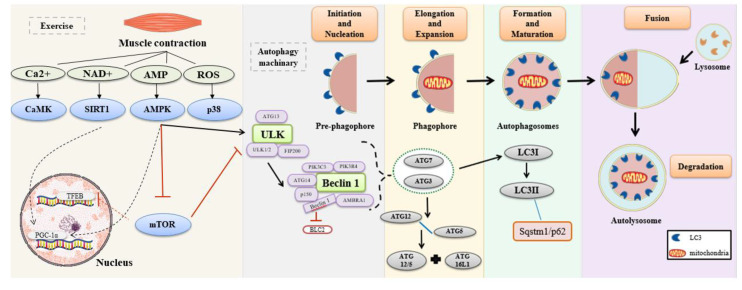
Figure 1.
Autophagy pathway process. Muscle contraction increases the levels of Ca2+, adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), adenosine monophosphate (AMP), and reactive oxygen species (ROS). These molecules activate their downstream effectors, which initiates autophagy activation. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activates autophagy induction complex by phosphorylation of unc-51-like autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1). The process begins with the formation of autophagic protein complex ULK (ULK1/2 + ATG13 + FIP200). Thereby, the mechanism initiation and activation of a second complex occur, named Beclin 1 (PIK3C3 P1K3R4+ Beclin 1 + ATG14 + p150 + Ambra 1). In this stage, Beclin 1 is dissociated from BCL-2, and this dissociation is responsible for the conduction of the Beclin 1 complex to the phagophore membrane, starting the nucleation. In sequence, activation of ATG7 occurs. ATG7 and ATG10 mediated the binding of ATG12-ATG5 conjugate to an ATG16L1 dimer. The ATG7 and ATG3 proteins generate the phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)-conjugation of LC3I, creating the LC3II, and producing the closure of phagophore in autophagosomes. The LC3II interacts with Sqstm1/p62. In sequence, the fusion occurs with the lysosome to form the autolysosome for degradation [29,30]. Solid and dashed black arrows activate the molecule or the complex. T red arrow inhibit the molecule or the complex