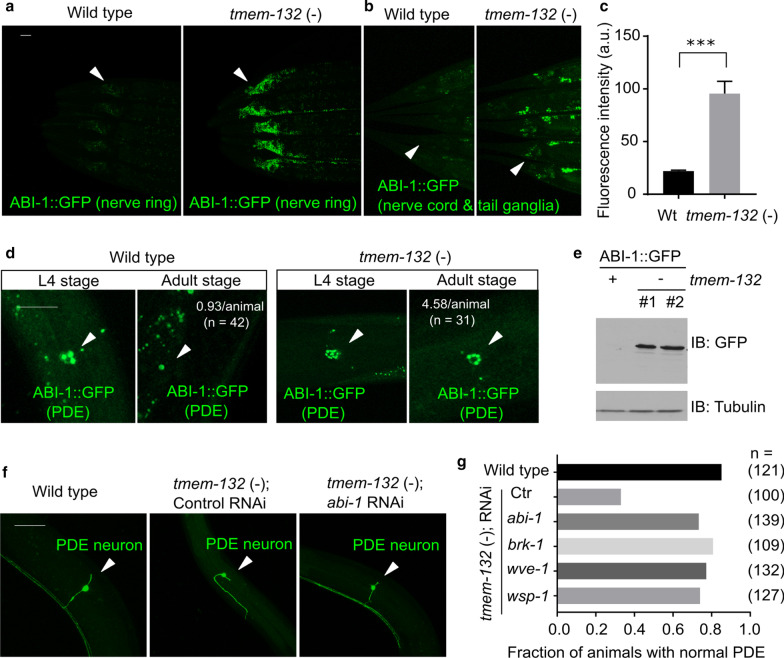
Fig. 6.
C. elegans TMEM-132 acts through WRC to regulate neuronal morphology. a, b Exemplar confocal fluorescent images showing increased abundance of neuronal ABI-1::GFP in tmem-132 deficient C. elegans. The rab-3 promoter-driven expression of abi-1::GFP was prominent in both nerve ring (arrow head in a) and tail ganglia (arrow head in b) areas of tmem-132 null animals but not wild type. c Quantification of fluorescence intensity of ABI-1::GFP in tmem-132 null and wild-type animals. d Exemplar confocal fluorescent images showing increased abundance of ABI-1::GFP in the PDE neurons of tmem-132 null, compared with wild type animals. Up-regulation of ABI-1::GFP in PDE was particularly prominent in young adult stage animals, compared with larval L4 stage animals. The average number of ABI-1::GFP puncta were noted for adult stages. e Exemplar Western blot showing increased abundance of ABI-1::GFP in total lysate of tmem-132 null animals, compared with wild type. Two independent deletions (#1, dma317; #2, dma318) produced similar effects. f Exemplar confocal fluorescence images showing abnormal PDE morphology in tmem-132 nulls, and rescued PDE morphology in tmem-132 nulls with treatment of abi-1 RNAi. g Quantification of fraction of animals with normal PDE morphology under indicated genetic conditions. abi-1, brk-1, wsp-1 and wve-1 encode components of WAVE or WAVE-like complex and their reduction-of-function by RNAi partially rescued abnormal PDE morphology of tmem-132 null animals. Scale bars: 50 µm. ***Indicates P < 0.001 (n = 5, repeated in at least three independent experiments)