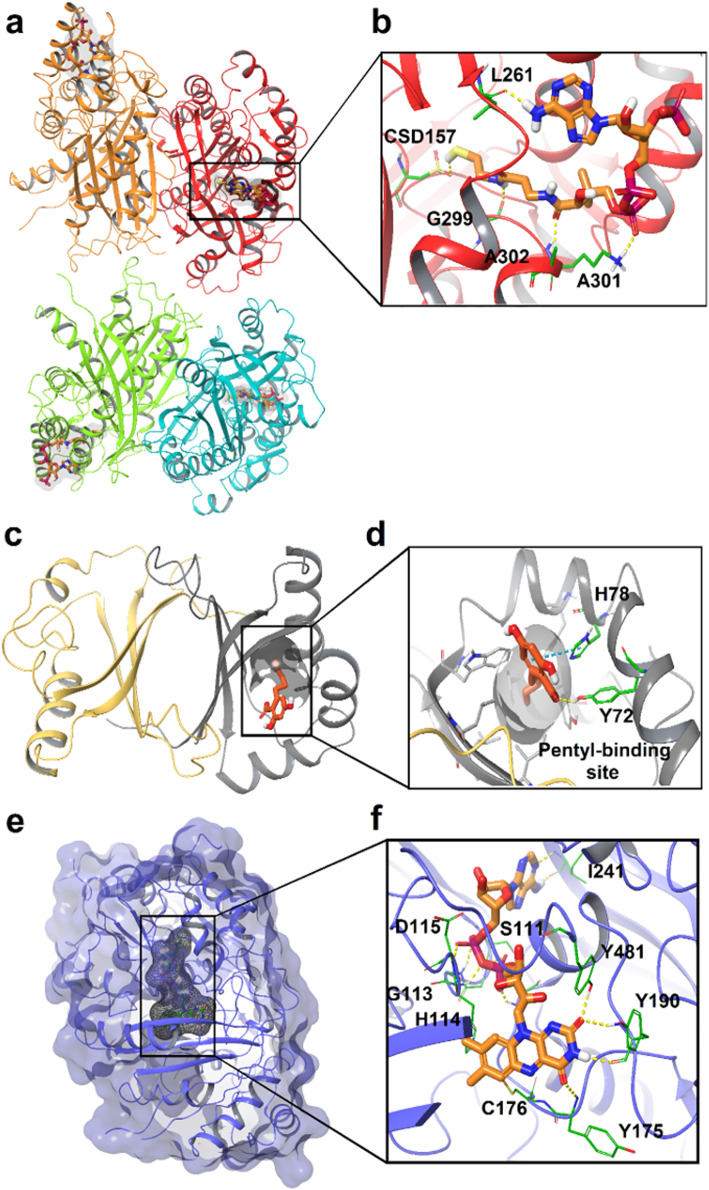
Fig. 3.
X-ray diffraction structures of three key enzymes implicated in cannabinoid biosynthesis. Key active site residues are highlighted in green, and interaction diagrams, generated by the authors using the Schrödinger computational software suite (Maestro 2020), of a) tetrameric tetraketide synthase (TKS) from C. sativa in complex with CoenzymeA (CoA, 6GW3), CoA is orange, with the four tetramers in red, orange, light green and cyan respectively (Kearsey et al. 2020); b) expansion of the active site; c) Olivetolic acid cyclase (OAC) from C. sativa (5BO9) (Yang et al. 2016), the pentyl-binding pocket and its key residues are gray, olivetolic acid (OLA) is orange, chain A is gray and chain B is in light orange; d) expansion of the active site, inverted; e) tetrahydrocannabinolic acid synthase (THCAS) from C. sativa (3VTE) bound to flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and without ligand. FAD is orange and the protein navy; and f) expansion of the active site (Shoyama et al. 2012)