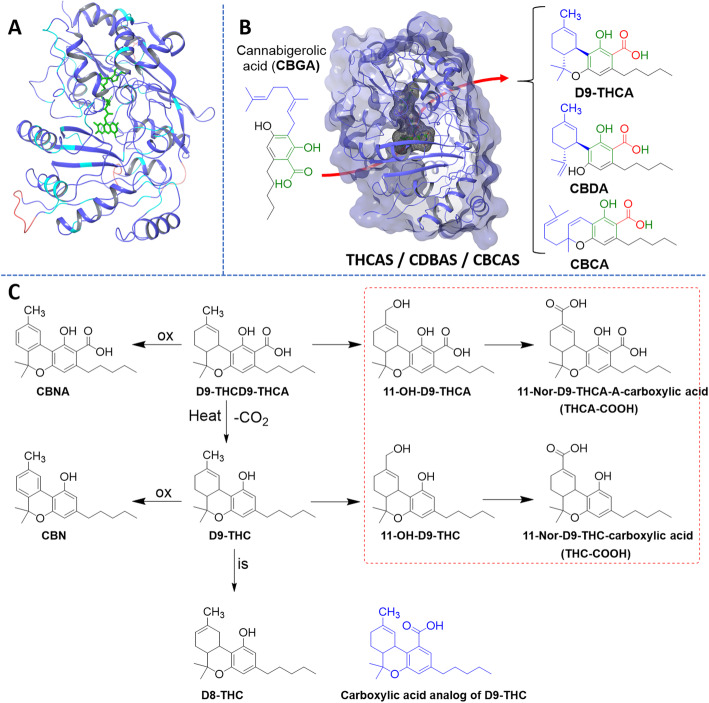
Fig. 6.
Comparison of cannabidiolic acid synthase (CBDAS) and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid synthase (THCAS) and the metabolism of cannabinoids. a Homology model of CBDAS developed from THCAS (3VTE); residues conserved from THCAS are purple while variant residues are cyan, sequence insertions are red, and FAD is green; b active site of these enzymes highlighted with a cartoon showing conversion to tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA); c experimentally demonstrated oxidation (ox) and isomerization (is) reactions and metabolic fates (encircled) for Δ9-THCA and Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC)