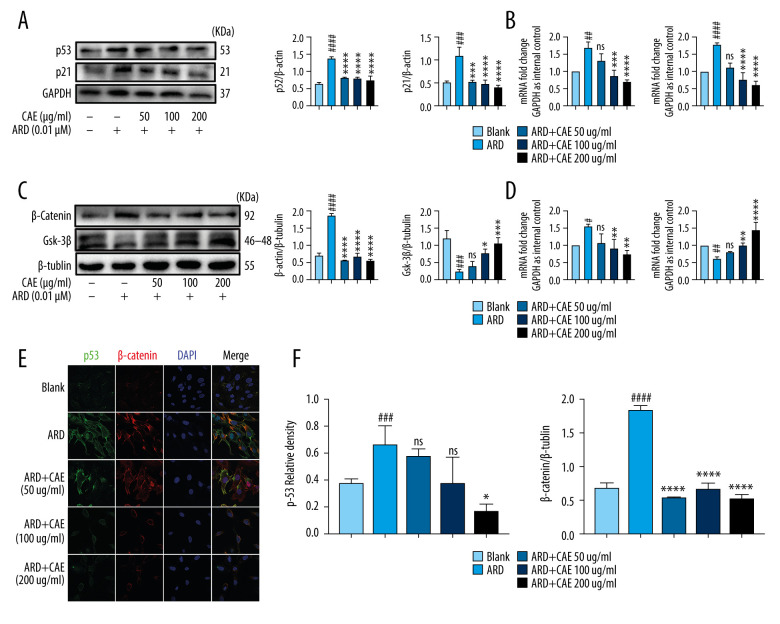
Figure 3.
Citrus alkaline extracts (CAE) inhibited the expression of p53 and β-catenin in A549 cells. (A) The analysis of p53and p21 in A549 cells by western blot. Each group was assessed in triplicate, and experiments were repeated 3 times. Bar graphs show the relative quantification. ### P<0.001, #### P<0.0001 vs Blank; *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001 vs Adriamycin RD (ARD). (B) Real-time qPCR analysis of genes; relative expression of p53 and p21. ## P<0.01, #### P<0.0001 vs Blank; * P<0.05, **** P<0.0001, and ns=not significant vs ARD. (C) The analysis of β-catenin and GSK-3β in A549 cells by western blot. Each group was assessed in triplicate, and experiments were repeated 3 times. Bar graphs show the relative quantification, ## P<0.01 vs Blank, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, and ns=not significant vs ARD. (D) Real-time qPCR analysis of genes, relative expression of p16. ### P<0.001 vs Blank, * P<0.05, *** P<0.001, and **** P<0.0001 vs ARD. (E, F) Immunofluorescence staining of p53 and β-catenin. DAPI was used to stain the nucleus. Scale bar, 50μm; ### P<0.001 vs Blank, * P<0.05, *** P<0.001, and ns=not significant vs ARD.