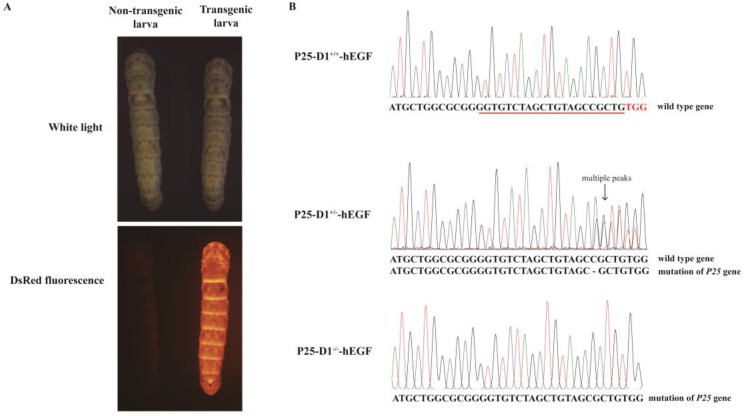
Figure 4.
Production of transgenic silkworms in a P25 gene knockout background. (A) Screening for positive transgenic silkworms by red fluorescence detection. (B) Sequencing of PCR products: sequencing of silkworm exuviation genomic DNA to detect the genotype at the P25 locus. The sequence underlined in red in the P25-D1+/+-hEGF group (upper) was the target site of sgRNA (small guide RNA) for CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/an associated protein (Cas9)) editing in our previous research, and the three bases TGG in red was the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence for Cas9 recognition. The multiple chromatogram peaks at the region flanking the PAM sequence in the P25-D1+/−-hEGF group (middle) suggests the successful generation of a heterozygous P25 gene mutant (black hyphen in the sequence represents the deleted base). The single peak in the chromatogram with a different sequence from wild type at the region flanking the PAM sequence in the P25-D1−/−-hEGF group (bottom) suggests the generation of the homozygous P25 gene mutant.