Figure 3.
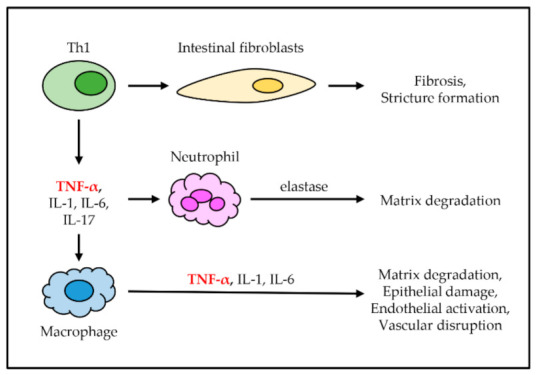
The role of TNF-α in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). TNF-α is secreted from Th1 cells along with other cytokines. These cytokines cause the accumulation of immune cells, including intestinal fibroblasts, neutrophils, and macrophages in the gut. Intestinal fibroblasts cause fibrosis and stricture formation. Neutrophils secrete elastase, which causes intestinal matrix degradation. Macrophages produce more inflammatory cytokines, which causes intestinal matrix degradation, epithelial damage, endothelial activation, and disruption.
