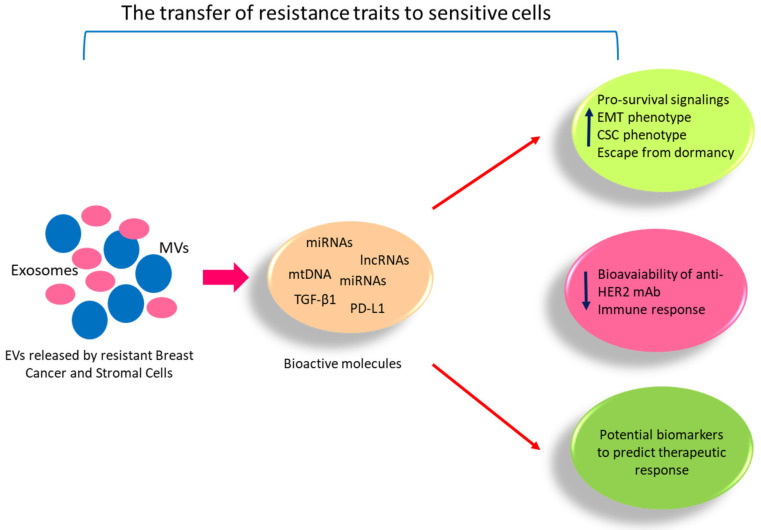
Figure 2.
The proposed function of EVs secreted by breast cancer or stromal cells in endocrine treatment resistance. EVs, by transferring their cargo in sensitive breast cancer cells, can confer traits of hormonal resistance by inducing signaling pathways involved in survival, migration, invasion, epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), in sustaining the cancer stem cell-like (CSC) phenotype and escape from dormancy. EVs can reduce the bioavailability of anti-HER2 mAb and immune evasion promoting resistance to targeted therapy to overcome endocrine therapies’ failure. Finally, evaluation of the molecular cargo of circulating EVs has promising value to discover potential biomarkers to predict the therapeutic response in ER-positive breast cancer patients.