Figure 4.
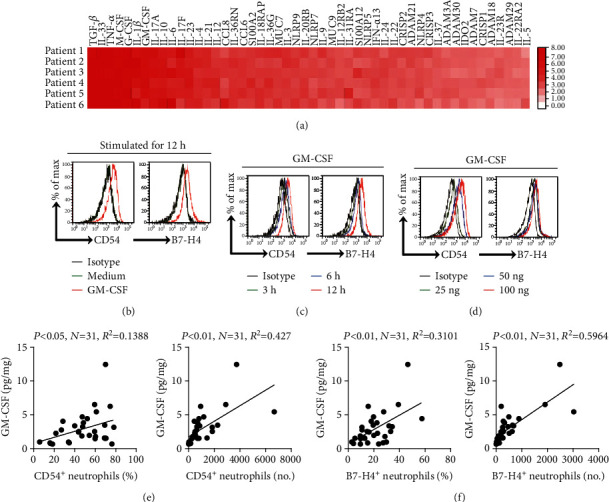
GM-CSF activates neutrophils and induces B7-H4 expression on neutrophils. (a) Clustering of microarray data for the expression of 50 proinflammatory cytokine genes in human tumor tissues from 6 GC patients. (b) Expressions of CD54 and B7-H4 on neutrophils exposed to GM-CSF (100 ng/ml), or to medium control for 12 h. Black: isotype control. (c) Expressions of CD54 and B7-H4 on neutrophils exposed to GM-CSF (100 ng/ml) for 3, 6, or 12 h. Black: isotype control. (d) Expressions of CD54 and B7-H4 on neutrophils exposed to GM-CSF (25, 50, or 100 ng/ml) for 12 h. Black, isotype control. (e) The correlations between GM-CSF and CD54+ neutrophils in GC tumors were analyzed. Results are expressed as the percentage of CD54+ neutrophils in neutrophils or the number of CD54+ neutrophils per million total cells and GM-CSF concentration in GC tumor tissues. (f) The correlations between GM-CSF and B7-H4+ neutrophils in GC tumors were analyzed. Results are expressed as the percentage of B7-H4+ neutrophils in neutrophils or the number of B7-H4+ neutrophils per million total cells and GM-CSF concentration in GC tumor tissues. Each dot in (e) and (f) represents 1 patient.
