Figure 6.
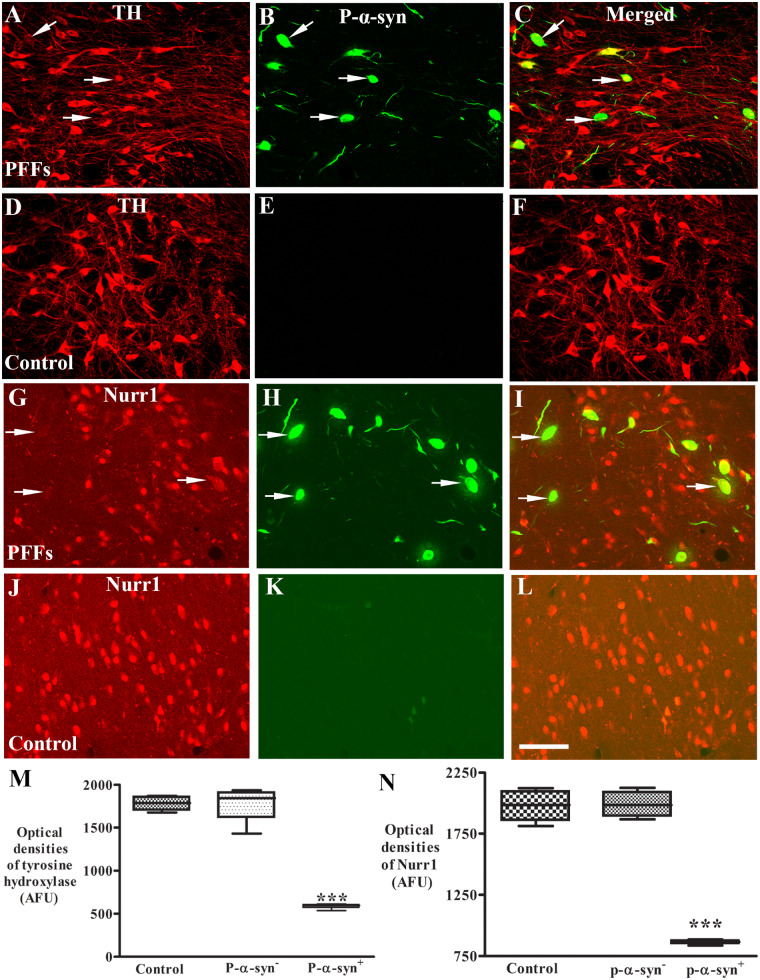
Laser confocal microscopic images of substantia nigra. Images are from monkeys receiving PFFs (A–C and G–I) and sham surgery (control; D–F and J–L) illustrating tyrosine hydroxylase (TH: red; A and D), Nurr1 (red; G and J), phosphorylated α-syn (P-α-syn: green; B, E, H and K), and the co-localization (merged; C, F, I and L). Note that TH immunofluorescence intensity was severely diminished (arrows; A and C) in the neurons with p-S129-α-syn (arrows; B and C) immunoreactive inclusions but not in neurons without P-α-syn-immunoreactive inclusions in monkeys received α-syn PFFs. Similarly, Nurr1 immunofluorescence intensity was severely diminished in the neurons (arrows; G and I) with p-α-syn immunoreactive inclusions (arrows; H and I) but not in neurons without P-α-syn immunoreactive inclusions. In contrast, no P-α-syn immunoreactive inclusions were observed in monkeys with sham surgery (E and K). Scale bar in L = 110 μm (applies to all). Quantitative measurement further revealed that the optic densities of TH (M) and Nurr1 (N) were significantly decreased in the neurons with P-α-syn immunopositive (P-α-syn+) but not in neurons with P-α-syn immunonegative (P-α-syn-) inclusion as compared with monkeys with sham surgery. ***P < 0.001, compared with sham surgery. AFU = arbitrary fluorescence units.