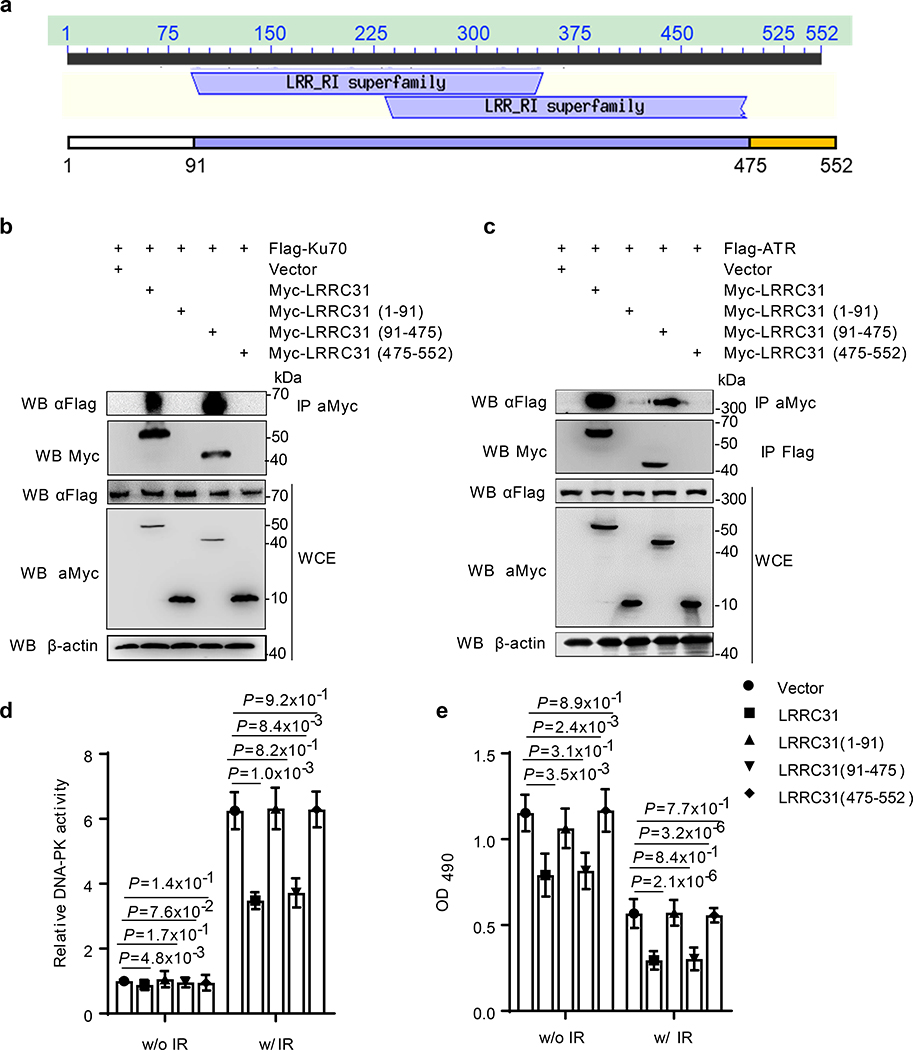
Fig. 4: Characterization of LRRC31 function motifs.
a, Analysis of the architecture of LRRC31. b,c, Co-IP analyses of the LRR superfamily domains (91–475) responsible for the interaction of LRRC31 with Ku70 (b) and ATR (c). Two biologically independent experiments were performed with similar results obtained. Unprocessed immunoblots are shown in Source Data Fig. 4. d,e, Characterization of the indicated domains within LRRC31 on DNA-PKcs activation (d) and cell proliferation (e) with the indicated treatments and irradiation at 4 Gy. Data show the mean ± s.d. (n=3 biologically independent experiments). Statistical analysis was performed using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. Statistical calculations source data are included in Source Data 4.c.