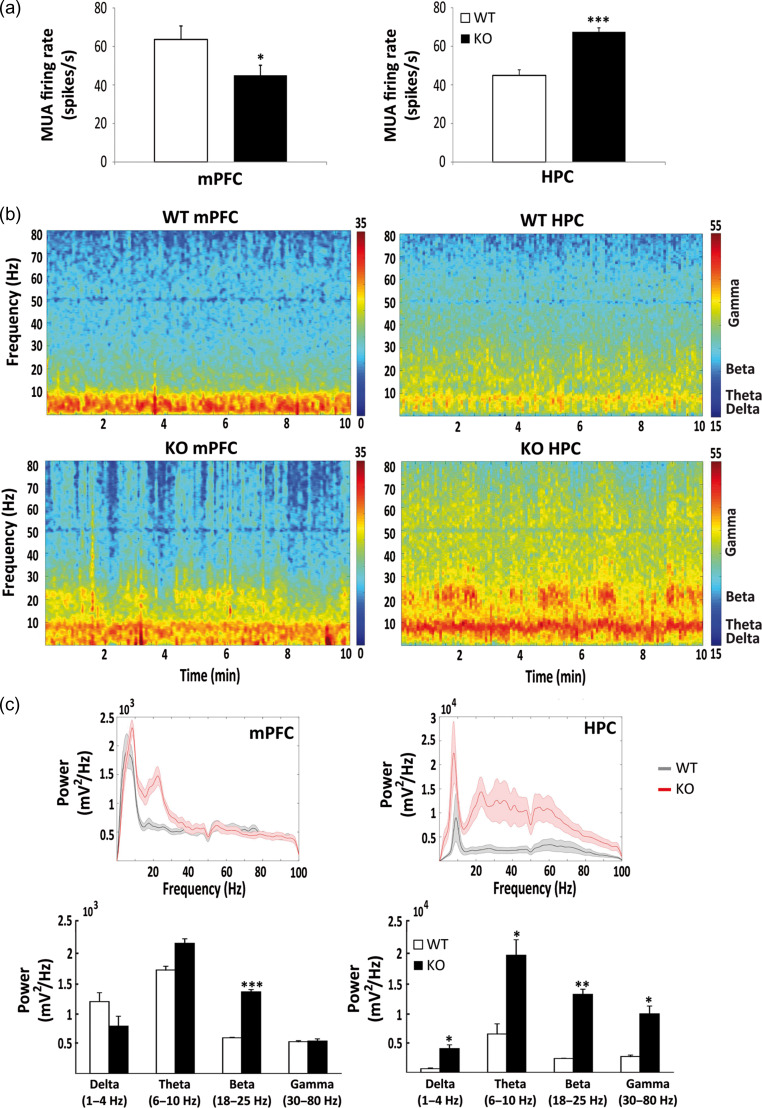
Figure 5.
Electrophysiological recordings in male WT and KO mice. Mean firing rate of multiunit activity (MUA) recorded simultaneously in the prelimbic cortex (mPFC) and CA1 (HPC) in freely moving male WT (n = 4) and KO (n = 3) mice (a). MUA was decreased in the mPFC (*P < 0.05) and increased in the HPC (***P < 0.001) of KO with respect to WT mice. Representative examples of spectrograms for WT and KO mice, showing the average power of the different frequency bands during 10 min of recordings (b). Red indicates larger power, which is markedly exacerbated in KO mice at all frequencies analyzed. Average power spectra in WT (black) and KO (red) mice (c). Note the different scale for mPFC and HPC plots. Quantification of power for the different oscillations shows that beta is significantly increased in KO with respect to WT mice in both areas (***P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, respectively), while delta, theta, and gamma are increased in KO versus WT only in the HPC (P < 0.05) (Student’s t-test).