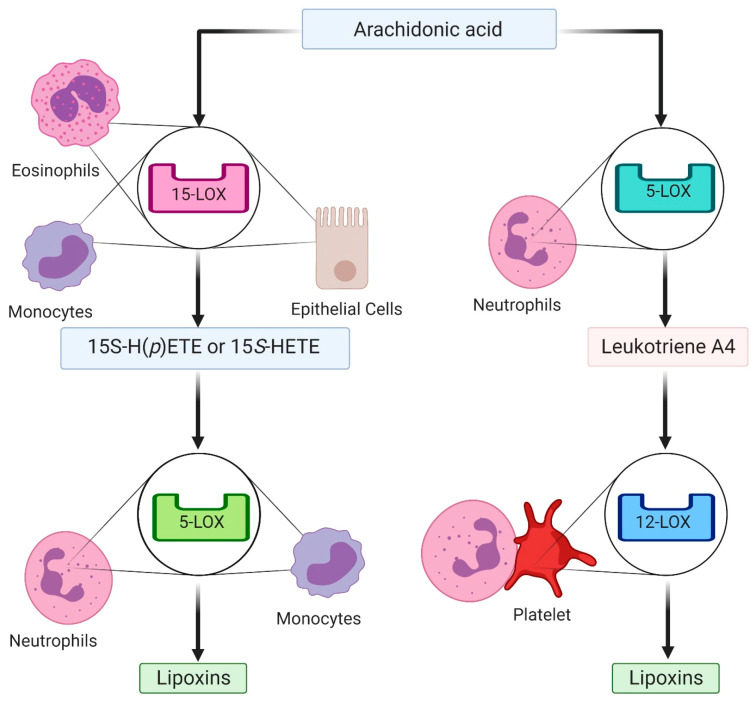
Figure 1.
Arachidonic acid-derived specialized pro-resolving mediator synthesis. Synthesis of the specialized pro-resolving mediator, lipoxin, requires transcellular biosynthesis (left side). Arachidonic acid receives an oxygen from 15-lipoxygenase (LOX), generating either 15S-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15S-H(p)ETE) or 15S-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15S-HETE). These metabolites are taken up by neutrophils where 5-LOX generates 5,6-epoxytetraene, an unstable molecule which is hydrolysed into lipoxins. Arachidonic acid can also be metabolized by neutrophils into leukotriene A4 (right side). Upon neutrophil-platelet binding, leukotriene A4 is converted into lipoxins by platelet 12-LOX.