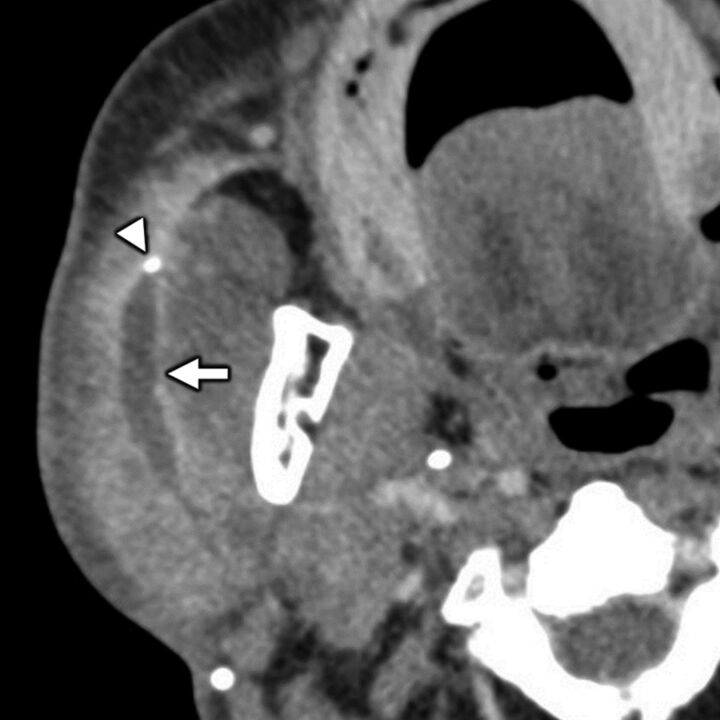
FIG 9.
Benign parotid pathology presenting with secondary otalgia. Axial contrast-enhanced CT in a 75-year-old man with right-sided ear pain shows obstructive calculous parotitis and sialodochitis with marked intraparotid ductal dilation (white arrow) and wall enhancement upstream of an obstructing sialolith (white arrowhead). Referred otalgia from intraparotid pathologies is thought to occur via the auriculotemporal nerve, a branch of CN V3.