Figure 2.
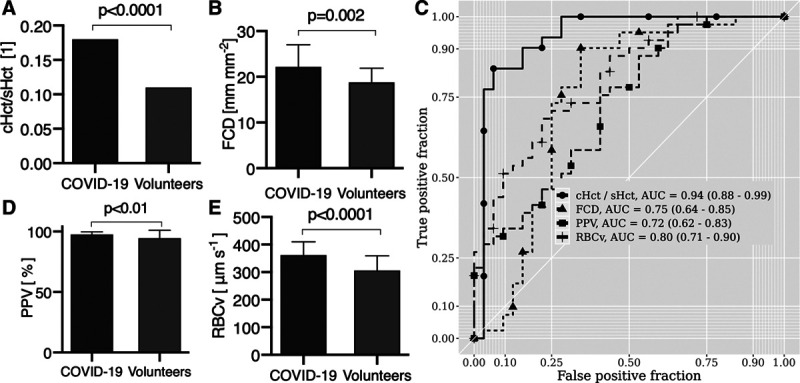
Analysis of the microhemodynamics of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients in comparison with those of the volunteers. COVID-19 patients had higher ratio capillary-to-systemic hematocrit (cHct/sHct) ratio (A) than in volunteers and higher functional capillary density (FCD) (B) than the volunteers. C, There was no evidence of plugged vessels in the COVID-19 patients as evidenced by a proportion of perfused vessel (PPV) > 94% in both groups. D, RBC velocity (RBCv) was significantly higher in COVID-19 patients than in the volunteers. E, Receiver-operating-characteristic curve analysis of the different microcirculatory hemodynamic parameters identifies cHct/sHct and RBCv as the parameters with the highest specificity and sensitivity for distinguishing the COVID-19 patients from the healthy volunteers. AUC = area under the curve.
