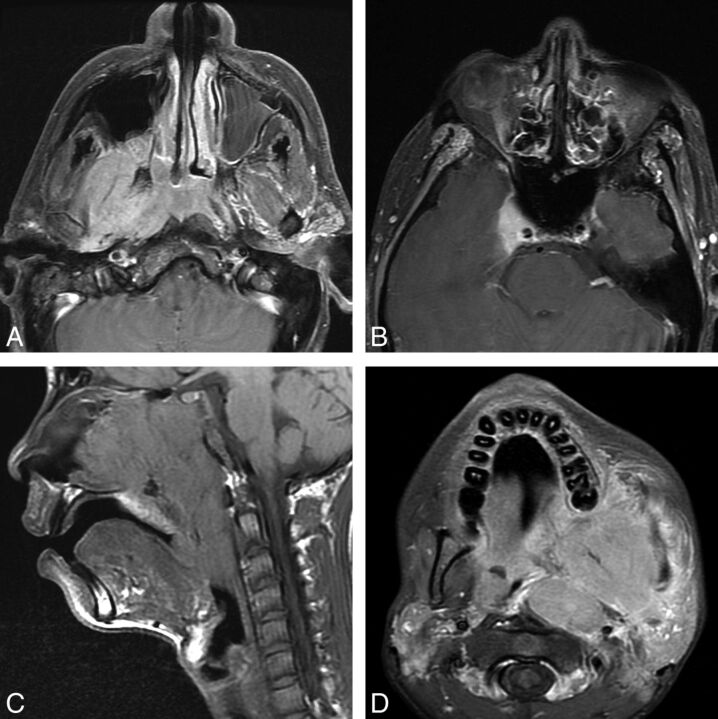
Fig 3.
Two patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. A and B, A 64-year-old man with a nasopharyngeal mass found incidentally on PET/CT and determined to be EBV(+) undifferentiated nonkeratinizing carcinoma. Axial T1 postcontrast fat-saturated images (A and B) demonstrate an asymmetric nasopharyngeal mass with lateral extension to the right masticator space lateral pterygoid muscle. In the seventh edition, this would be T4 disease; however, in the eighth edition, this is only T2 disease. Note however that in this patient, there is also involvement of the pterygoid plates, which is now clarified as T3 disease, and superior extension to the right cavernous sinus, which is T4 disease in both AJCC Cancer Staging Manual seventh and eighth editions. C and D, A 15-year-old boy presenting with epistaxis and a large mass arising from the nasopharynx determined to be EBV(+) undifferentiated nonkeratinizing carcinoma. Sagittal T1 (C) shows the large mass filling the nasopharynx, extending inferiorly to the oropharynx and anteriorly to the nasal cavity. Axial postcontrast T1 with fat saturation (D) shows lateral extension of the mass into the masticator space but also to the left parotid gland. In the eighth edition, involvement of the parotid gland or extension of tumor beyond the lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid muscle determines T4 status.