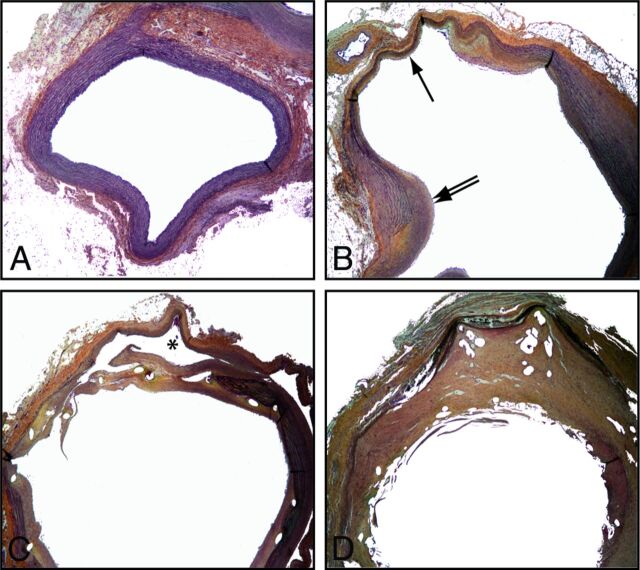
Fig 4.
Pathology of untreated, stented, and flow-diverted fusiform aneurysms. The standard saccular model shows a subclavian of normal diameter with a continuous elastic lamina and no neointima formation (A). In comparison, the complex fusiform aneurysm is composed of a dilated thinned wall with a discontinuous media (black arrow) and neointima formation (double arrow). In case of treatment failure with HPS (C), the stent struts were covered with a thin, discontinuous neointima with leaks responsible for the residual aneurysm (partially shown, black asterisk). Successful occlusion of fusiform aneurysms by an FD (D) was associated with thick and complete neointimal coverage of the FD. (Movat staining, original magnification ×50.)