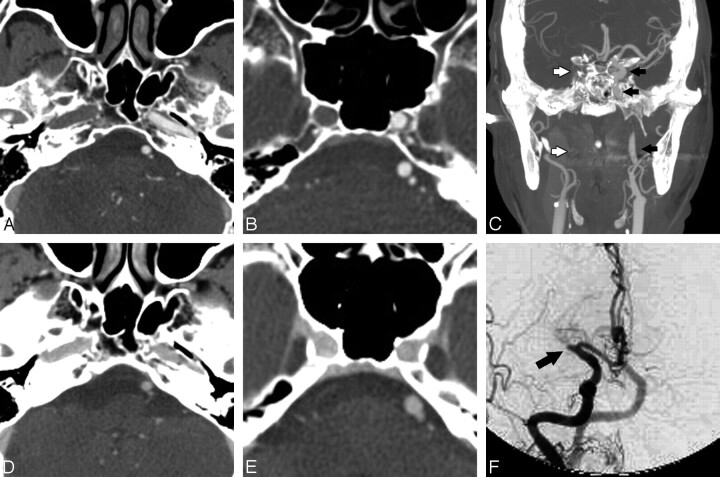
Fig 5.
A 79-year-old woman with left hemiparesis. A−C, CTA shows nonopacification and apparent occlusion of the entire right ICA, from its origin to the carotid terminus. Compare the normally opacified left ICA (black arrows) with the nonopacified right side (white arrows in C denote the expected course of the right ICA). D and E, Axial contrast-enhanced images, however, show opacification and confirm patency of the right ICA at comparable levels. F, Conventional angiogram obtained 4 hours later (anteroposterior [AP] view right carotid injection) confirms patency of the entire intracranial ICA but reveals an abrupt cutoff of the proximal M1 segment (arrow), consistent with occlusion. Nonopacification on CTA is attributed to the sluggish flow resulting from the M1 occlusion on the right side.