Fig 3.
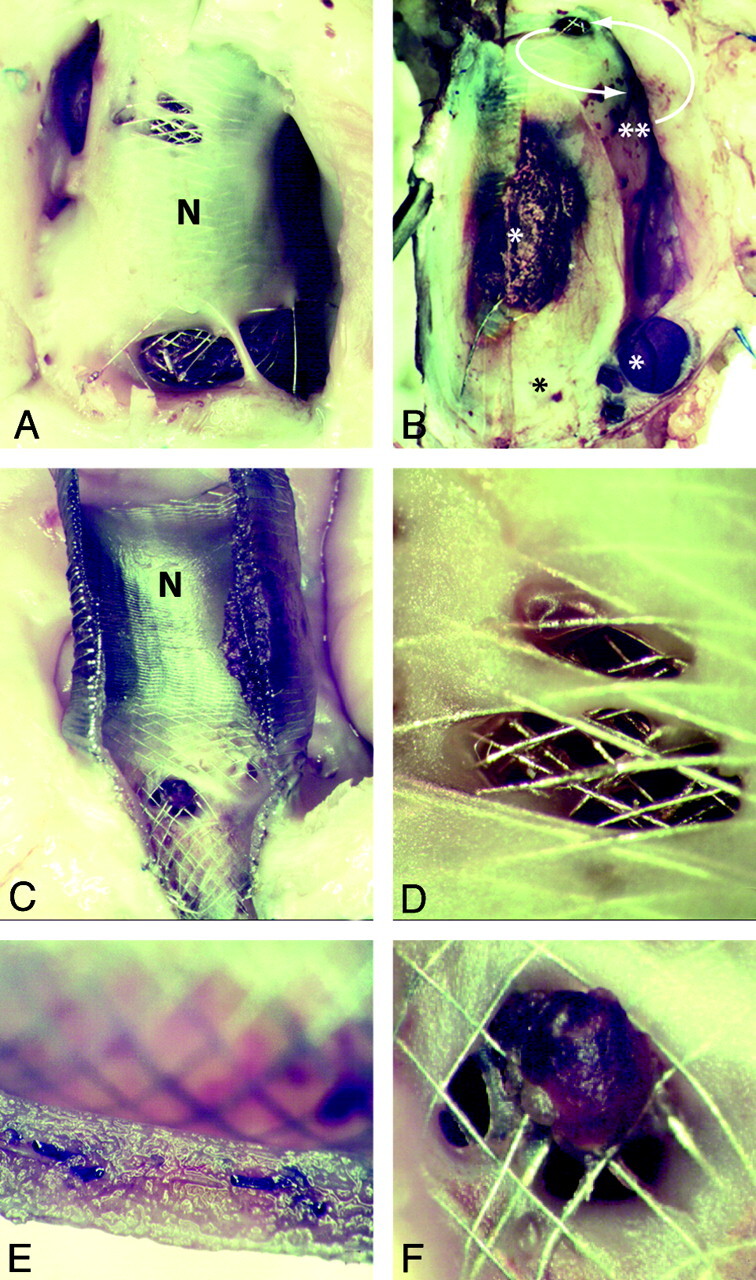
Residual aneurysm, neointima formation, and leaks. Note patent, open aneurysms (A; corresponding to Fig 2E), when the aneurysm serves as a reservoir for feeding branches. When branches are absent (B) the aneurysm is almost completely occluded, with pouches containing thrombus in various stages or organization (*). A small crescentic remnant, fed by a small leak (curved arrows) is present (**; aneurysm corresponding to Fig 2F). The FDs are covered with neointima both inside and outside (C), and leaks penetrate both neointimal layers covering the stents (D and E). There is good neointimal coverage of the stent struts apposed to the parent artery (E). Note patent arterial branch ostium but partially covered with neointimal tissue and organizing clot (F).
