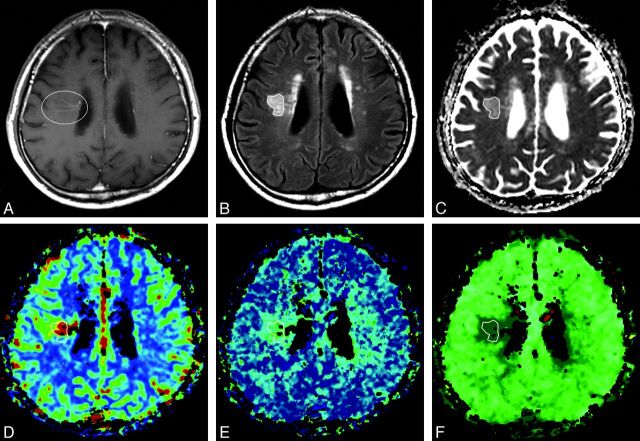
Fig 1.
A 60-year-old man with blurred vision and headache. A, Postcontrast T1-weighted axial image shows a dilated medullary vein draining into the subependymal collecting vein in the right corona radiata (circle), representing a developmental venous anomaly. B, Abnormal signal intensity is seen in the area of the DVA (polygon) on the axial T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging. C, Apparent diffusion coefficient. D, Relative cerebral blood volume. E, Relative mean transit time. F, Time-to-peak map demonstrates increased values of the corresponding area compared with contralateral normal white matter. These findings suggest that the nature of the SI abnormalities around DVAs is vasogenic edema with congestion and delayed perfusion.