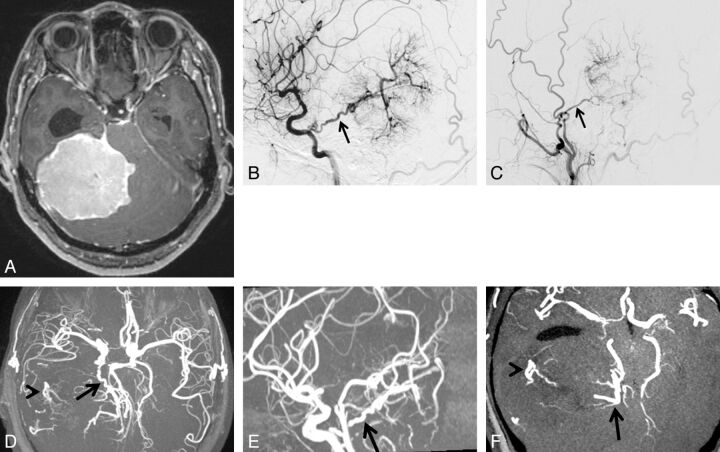
Fig. 2.
A 49-year-old woman with tentorial meningioma. A, Axial contrast-enhanced 3D turbo field echo image showing a large enhanced mass in the supra- to infratentorial regions. B, DSA (lateral projection from the right internal carotid artery) reveals a tumor fed primarily by the tentorial artery of the meningohypophyseal trunk (arrow). Based on the surgical findings, the dural attachment was the tentorium cerebelli. C, DSA (lateral projection from the right external carotid artery) shows a tumor fed partially by the middle meningeal artery (arrow). The right middle meningeal artery was judged to be the secondary feeder. D, 3D TOF MRA (axial projection) depicts dilated branches from the right tentorial- (arrow) and middle meningeal arteries (arrowhead). E, 3D TOF MRA (sagittal projection) shows the dilated tentorial artery (arrow) from the meningohypophyseal trunk of the internal carotid artery. F, This axial partial MIP MRA shows tumor-feeding branches from the tentorial artery at the medial portion of the tumor (arrow) and from the middle meningeal artery at the lateral portion of the tumor (arrowhead). Both readers judged that the tentorial artery of the meningohypophyseal trunk was the primary feeder and that the dural attachment was the tentorium cerebelli.